Medial root of median nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:Upper limb anatomy]] | [[Category:Upper limb anatomy]] | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Brachial plexus.svg|Brachial plexus | |||
File:Gray809.png|Gray's Anatomy illustration 809 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 06:05, 3 March 2025
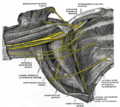
Medial root of median nerve is a term in anatomy that refers to one of the two roots that form the median nerve, a major nerve of the upper limb. The other root is the lateral root of median nerve. The medial root of median nerve is derived from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and contributes to the innervation of the forearm and hand.
Etymology
The term "medial root of median nerve" is derived from the Latin words "medius" meaning middle, "radix" meaning root, and "nervus" meaning nerve. Thus, the term literally means the middle root of the nerve.
Anatomy
The medial root of median nerve originates from the medial cord of the brachial plexus, which is formed by the anterior divisions of the lower and middle trunks of the brachial plexus. The medial root of median nerve joins with the lateral root of median nerve, which is derived from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, to form the median nerve.
The median nerve then travels down the arm and forearm, providing motor and sensory innervation to various structures. In the forearm, it innervates most of the flexor muscles, except for the flexor carpi ulnaris and the ulnar half of the flexor digitorum profundus. In the hand, it innervates the thenar muscles and the first two lumbricals.
Clinical significance
Damage to the medial root of median nerve can result in a variety of symptoms, depending on the severity and location of the injury. These may include weakness or paralysis of the muscles innervated by the median nerve, numbness or tingling in the area of skin supplied by the nerve, and pain in the arm or hand.
See also
References
<references />