Bicaudaviridae: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Archaea viruses]] | [[Category:Archaea viruses]] | ||
{{virus-stub}} | {{virus-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Bicaudavirus virion.jpg|Bicaudavirus virion | |||
File:ODD.Bic.Fig2.v2.png|ODD Bic Fig2 v2 | |||
File:ODD.Bic.Fig1 Acidianus two-tailed virus.jpg|ODD Bic Fig1 Acidianus two-tailed virus | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:44, 3 March 2025
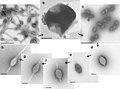
Bicaudaviridae is a family of viruses that infect archaeal hosts. The family name is derived from the Latin bicauda, meaning "two tails", which refers to the unique morphology of the virions in this family.
Taxonomy[edit]
The family Bicaudaviridae consists of a single genus, Ampullavirus, which in turn contains a single species, Halorubrum pleomorphic virus 6 (HRPV-6). This taxonomy is recognized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV).
Structure[edit]
Viruses in Bicaudaviridae are enveloped, with pleomorphic geometries. The virion has two tails, which gives the family its name. The diameter is around 70-90 nm, with a length of 200-300 nm. The genome is linear, around 16 kb in length.
Life Cycle[edit]
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by budding, and tubule-guided viral movement. Archaea serve as the natural host.
Pathology[edit]
The viruses in this family infect halophilic archaea, specifically species in the genus Halorubrum. The impact of these infections on the host organisms is not well understood.
References[edit]
<references />
External links[edit]
-
Bicaudavirus virion
-
ODD Bic Fig2 v2
-
ODD Bic Fig1 Acidianus two-tailed virus