Quinclorac: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{chemistry-stub}} | {{chemistry-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
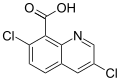
File:Quinclorac.svg|Quinclorac | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:06, 3 March 2025
Quinclorac is a selective, systemic herbicide used primarily for post-emergence control of broadleaf and grassy weeds in various crops. It is a member of the quinolinecarboxylic acid group of herbicides, which also includes quinmerac and quinoclamine. Quinclorac is used in a variety of crops including rice, maize, and wheat.
Chemistry[edit]
Quinclorac is a white crystalline solid with a slight odor. It is soluble in water and most organic solvents. The chemical formula for quinclorac is C10H5Cl2NO2, and its molecular weight is 241.06 g/mol. The compound is stable under normal conditions, but it can decompose when heated.
Mode of Action[edit]
Quinclorac acts by inhibiting the plant's ability to produce certain essential proteins, leading to the death of the plant. It is absorbed by the roots and foliage and is translocated throughout the plant. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the inhibition of auxin transport.
Uses[edit]
Quinclorac is used for the control of a wide range of broadleaf and grassy weeds in a variety of crops. It is particularly effective against crabgrass, a common weed in lawns and other turf areas. Quinclorac is also used in rice cultivation to control watergrass and barnyardgrass.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Quinclorac is moderately persistent in the environment, with a half-life in soil of 30 to 90 days. It has low toxicity to birds and mammals, but it can be toxic to some species of fish and aquatic invertebrates. Quinclorac can leach into groundwater and may pose a risk to aquatic ecosystems.
Health Effects[edit]
Exposure to quinclorac can cause irritation of the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Ingestion can cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Long-term exposure can lead to liver and kidney damage.
Regulation[edit]
In the United States, quinclorac is regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). It is classified as a Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP) due to its potential to contaminate groundwater.
See Also[edit]
-
Quinclorac