Mesotrione: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{agriculture-stub}} | {{agriculture-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Mesotrione == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Leptospermone.svg|Leptospermone | |||
File:Chemical_structure_of_sulcotrione.png|Chemical structure of sulcotrione | |||
File:Mesotrione.svg|Mesotrione | |||
File:Callistemon_citrinus_3.jpg|Callistemon citrinus | |||
File:mesotrione_synthesis.png|Mesotrione synthesis | |||
File:Mesotrione_use_USA.png|Mesotrione use in USA | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:58, 27 February 2025
Mesotrione is a selective pre and post-emergent herbicide that was introduced to the market by Syngenta in 2001. It is used to control broadleaf weeds and some annual grasses in corn crops. Mesotrione works by inhibiting the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD), which is essential for the production of carotenoids in plants.
Chemistry[edit]
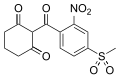
Mesotrione is a synthetic compound that is structurally similar to the natural product leptospermone, which is produced by the bottlebrush plant (Callistemon citrinus). The chemical formula of mesotrione is C14H13NO7S.
Mode of Action[edit]
Mesotrione inhibits the enzyme HPPD, which is involved in the biosynthesis of carotenoids in plants. Carotenoids are important for the protection of chlorophyll from photodegradation. When the production of carotenoids is inhibited, the chlorophyll is degraded by sunlight, which leads to the bleaching and death of the plant.
Use in Agriculture[edit]
Mesotrione is used in corn crops to control broadleaf weeds and some annual grasses. It can be applied pre-emergence or post-emergence. The product is usually applied in a tank mix with other herbicides to increase the spectrum of weed control.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Mesotrione has a low toxicity to mammals, birds, and fish. However, it can be harmful to non-target plants if it is applied in high concentrations or if it drifts off-target during application. The compound is moderately persistent in the soil, with a half-life of 14 to 50 days.
Resistance[edit]
Resistance to mesotrione and other HPPD inhibitors has been reported in some weed species, including waterhemp and Palmer amaranth. This resistance is often due to enhanced rates of herbicide metabolism in the resistant plants.

This article is a agriculture stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Mesotrione[edit]
-
Leptospermone
-
Chemical structure of sulcotrione
-
Mesotrione
-
Callistemon citrinus
-
Mesotrione synthesis
-
Mesotrione use in USA