Salsolinol: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Salsolinol == | |||
<gallery> | |||
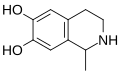
File:Salsolinol_v2.svg|Salsolinol structure | |||
File:Salsolinol_metabolism.svg|Salsolinol metabolism | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:07, 25 February 2025
Salsolinol is a tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid that is formed in the human body from dopamine and acetaldehyde. It is a neurotoxin and has been suggested to have a possible role in alcoholism.
Chemistry[edit]
Salsolinol is a tetrahydroisoquinoline, a type of alkaloid. It is formed in the body from the condensation of dopamine and acetaldehyde. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT).
Pharmacology[edit]
Salsolinol has been found to have neurotoxic effects. It is thought to cause damage to the dopaminergic neurons in the brain, which may contribute to the development of Parkinson's disease.
In addition to its neurotoxic effects, salsolinol has also been found to have rewarding effects. It has been suggested that it may contribute to the reinforcing effects of alcohol, and thus play a role in the development of alcoholism.
Role in Alcoholism[edit]
The role of salsolinol in alcoholism is not fully understood. Some studies have found that the levels of salsolinol in the body are increased after alcohol consumption, and that these levels are higher in individuals with alcoholism compared to those without. However, other studies have not found a clear link between salsolinol levels and alcohol consumption or alcoholism.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />