Berbamine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Berbamine == | |||
<gallery> | |||
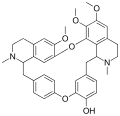
File:Berbamine_structure.svg|Berbamine structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:02, 25 February 2025
Berbamine is a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid derived from the Berberis species, particularly Berberis vulgaris. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for its anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Berbamine is a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid, which means it contains two benzylisoquinoline units linked together. Its chemical formula is C37H40N2O6.
Pharmacology[edit]
Berbamine has been shown to have several pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-microbial, and cardioprotective properties.
Anti-inflammatory[edit]
Berbamine has been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are proteins that promote inflammation. This makes it potentially useful in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Anti-cancer[edit]
Berbamine has been shown to inhibit the growth of various types of cancer cells, including leukemia, breast cancer, and lung cancer cells. It does this by inducing apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
Anti-microbial[edit]
Berbamine has been shown to have anti-microbial properties, making it potentially useful in the treatment of infections.
Cardioprotective[edit]
Berbamine has been shown to protect the heart from damage caused by ischemia, a condition in which the heart muscle is starved of oxygen.
Safety[edit]
While berbamine has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, its safety in humans has not been thoroughly studied. As with any supplement, it should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider.