Sacrotuberous ligament: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:Orthopedics]] | ||
[[Category:Medical Encyclopedia]] | [[Category:Medical Encyclopedia]] | ||
== Sacrotuberous_ligament == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray319.png|Gray319 | |||
File:Gray542.png|Gray542 | |||
File:Gray1077.png|Gray1077 | |||
File:Gray1243.png|Gray1243 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 20:56, 25 February 2025
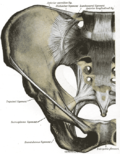
Sacrotuberous ligament is a significant structure in the human body that plays a crucial role in the stability of the pelvis. It is a flat, triangular ligament that extends from the sacrum and coccyx to the ischial tuberosity, hence the name 'sacrotuberous'.
Anatomy[edit]
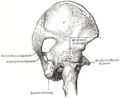
The sacrotuberous ligament is a strong, triangular ligament that extends from the lower part of the posterior surface of the sacrum and the upper part of the coccyx to the inner margin of the tuberosity of the ischium. It is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis.
Function[edit]
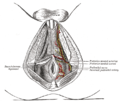
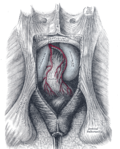
The sacrotuberous ligament serves as a critical stabilizer for the pelvis. It prevents the forward rotation of the sacrum, thus maintaining the stability of the pelvis. It also provides attachment for several muscles, including the gluteus maximus and coccygeus.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The sacrotuberous ligament can be involved in various pathological conditions. For instance, it can be affected in piriformis syndrome, a neuromuscular disorder that occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed or otherwise irritated by the piriformis muscle causing pain, tingling, or numbness in the buttocks.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />