Agrifood systems: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
|||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{agriculture-stub}} | {{agriculture-stub}} | ||
{{nt}} | {{nt}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
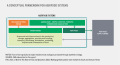
File:A_conceptual_framework_for_agrifood_systems.svg|A conceptual framework for agrifood systems | |||
File:Agrifood_systems_emissions_2021.svg|Agrifood systems emissions 2021 | |||
File:Quantified_hidden_costs_of_agrifood_systems_by_cost_category_(left)_and_subcategory_(right),_2020.svg|Quantified hidden costs of agrifood systems by cost category (left) and subcategory (right), 2020 | |||
File:DIETS_LOW_IN_WHOLE_GRAINS_AND_FRUITS_AND_HIGH_IN_SODIUM_ARE_THE_LEADING_DIETARY_RISKS_CONTRIBUTING_TO_GLOBAL_HEALTH_HIDDEN_COSTS.svg|Diets low in whole grains and fruits and high in sodium are the leading dietary risks contributing to global health hidden costs | |||
File:The_status_of_women_in_agrifood_systems_-_Overview.pdf|The status of women in agrifood systems - Overview | |||
File:The_State_of_Food_and_Agriculture_2021._Making_agrifood_systems_more_resilient_to_shocks_and_stresses,_In_brief.pdf|The State of Food and Agriculture 2021. Making agrifood systems more resilient to shocks and stresses, In brief | |||
File:Robust_transport_networks_support_agrifood_systems%27_resilience.pdf|Robust transport networks support agrifood systems' resilience | |||
File:Ensuring_economic_access_to_healthy_diets_during_times_of_crisis.pdf|Ensuring economic access to healthy diets during times of crisis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:07, 25 February 2025
Agrifood Systems refer to the set of activities and processes involved in the production, processing, distribution, and consumption of food. These systems encompass a wide range of components, including agriculture, food science, nutrition, and environmental sustainability.
Overview[edit]
Agrifood systems are complex networks that involve various stakeholders, including farmers, processors, distributors, retailers, consumers, and policymakers. These systems are influenced by a variety of factors, such as economic conditions, technological advancements, societal trends, and environmental changes.
Components of Agrifood Systems[edit]
Agriculture[edit]
Agriculture is the foundation of agrifood systems. It involves the cultivation of plants and the rearing of animals for food, fiber, medicinal plants, and other products used to sustain and enhance human life.
Food Science[edit]
Food science is a multidisciplinary field that applies the principles of biology, chemistry, and physics to the study of food. It plays a crucial role in the development of new food products, the improvement of food quality, and the assurance of food safety.
Nutrition[edit]
Nutrition is the science that interprets the interaction of nutrients and other substances in food in relation to maintenance, growth, reproduction, health, and disease of an organism. It includes food intake, absorption, assimilation, biosynthesis, catabolism, and excretion.
Environmental Sustainability[edit]
Environmental sustainability in agrifood systems involves the implementation of farming practices and food production methods that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially responsible.
Challenges in Agrifood Systems[edit]
Agrifood systems face several challenges, including climate change, food insecurity, soil degradation, and biodiversity loss. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions, such as sustainable farming practices, improved food processing technologies, and effective food distribution strategies.
Future of Agrifood Systems[edit]
The future of agrifood systems lies in the adoption of sustainable agriculture practices, the development of climate-smart agriculture strategies, and the promotion of healthy diets and sustainable consumption patterns.
This article is a agriculture stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
A conceptual framework for agrifood systems
-
Agrifood systems emissions 2021
-
Quantified hidden costs of agrifood systems by cost category (left) and subcategory (right), 2020
-
Diets low in whole grains and fruits and high in sodium are the leading dietary risks contributing to global health hidden costs
-
The status of women in agrifood systems - Overview
-
The State of Food and Agriculture 2021. Making agrifood systems more resilient to shocks and stresses, In brief
-
Robust transport networks support agrifood systems' resilience
-
Ensuring economic access to healthy diets during times of crisis