Sebaceous gland: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
== Sebaceous gland == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Hair_follicle-en.svg|Hair follicle diagram | |||
File:Skin.png|Skin diagram | |||
File:Base_of_Pilosebaceous_Unit_10x.JPG|Base of Pilosebaceous Unit 10x | |||
File:Insertion_of_sebaceous_glands_into_hair_shaft_x10.jpg|Insertion of sebaceous glands into hair shaft x10 | |||
File:Gray893.png|Gray's Anatomy Plate 893 | |||
File:Gray944.png|Gray's Anatomy Plate 944 | |||
File:Scalp_cross_section_(negro).jpg|Scalp cross section | |||
File:407_Sebaceous_Glands.jpg|Sebaceous Glands | |||
File:Blausen_0811_SkinPores.png|Skin Pores | |||
File:Cheiromeles_torquatus.jpg|Cheiromeles torquatus | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:44, 23 February 2025
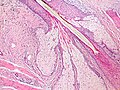
Sebaceous glands are small oil-producing glands present in the skin of mammals. They are usually attached to hair follicles and release a fatty substance, sebum, into the follicular duct and thence to the surface of the skin. The glands are distributed over the entire body with the exception of the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet; they are most abundant on the scalp and face.
Structure[edit]
Sebaceous glands are typically located in the dermis, the layer of skin that lies beneath the epidermis. They are usually connected to hair follicles, but they can also exist independently. The glands are composed of sebaceous cells that are filled with lipid droplets, and they are surrounded by a layer of epithelial cells.
Function[edit]
The primary function of sebaceous glands is to produce and release sebum, a type of oil that coats and protects the skin and hair. Sebum also has antimicrobial properties, which can help to protect the skin from bacterial and fungal infections. In addition, it helps to keep the skin moisturized and prevents it from drying out.
Clinical significance[edit]
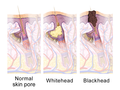
Sebaceous glands can be involved in a number of skin conditions, including acne, seborrheic dermatitis, and sebaceous cysts. Overactive sebaceous glands can lead to excessive oil production, which can result in acne. Conversely, underactive glands can lead to dry skin and hair.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
Sebaceous gland[edit]
-
Hair follicle diagram
-
Skin diagram
-
Base of Pilosebaceous Unit 10x
-
Insertion of sebaceous glands into hair shaft x10
-
Gray's Anatomy Plate 893
-
Gray's Anatomy Plate 944
-
Scalp cross section
-
Sebaceous Glands
-
Skin Pores
-
Cheiromeles torquatus