Quassia: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
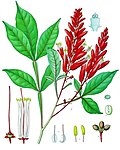
File:Quassia_amara_-_Köhler–s_Medizinal-Pflanzen-117.jpg|Quassia amara - Köhler's Medizinal-Pflanzen | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:36, 23 February 2025
Quassia is a plant genus in the family Simaroubaceae. The genus was named by Carl Linnaeus who named it after the first botanist to describe it: the Surinamese freedman Graman Quassi.
Quassia is used as a natural insecticide, for the production of bitter tonics and liqueurs, in traditional medicine.
Species[edit]
The genus includes the following species:
- Quassia amara L. – a shrub or rarely a small tree, native to Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, Colombia, Guyana, Suriname, Venezuela, French Guiana, Brazil, Peru, Bolivia; naturalized in Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands
- Quassia africana Baill. – Gabon, São Tomé, Príncipe
- Quassia bidwillii Benth. – Queensland, New South Wales
- Quassia indica (Gaertn.) Nooteboom – India, Sri Lanka, Andaman & Nicobar, Thailand, Myanmar, Vietnam, Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, Sumatra, Java, Lesser Sunda Islands, Sulawesi, Philippines, Moluccas, New Guinea, Bismarck Archipelago, Solomon Islands, Queensland, Fiji, Samoa, Tonga, Vanuatu, New Caledonia, Caroline Islands, Marianas, Taiwan
- Quassia sp. A – Gabon
- Quassia sp. B – Gabon
Uses[edit]
Quassia wood is used for making furniture. The bark and wood are used to make a bitter tonic and a liqueur. The plant is also used in traditional medicine for treating malaria, fever, and anorexia. It is also used as an insecticide.