Modulation: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Modulation == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Modulation_categorization.svg|Modulation categorization | |||
File:Amfm3-en-de.gif|AM and FM modulation | |||
File:Waterfall_AM.jpg|Waterfall AM | |||
File:Waterfall_FM.jpg|Waterfall FM | |||
File:baud.svg|Baud rate | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:10, 23 February 2025
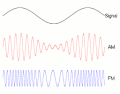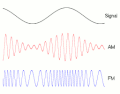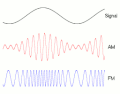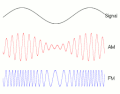
Modulation is a process that changes the properties of a carrier wave based on the characteristics of an input signal. This process is fundamental in telecommunication and signal processing.
Types of Modulation[edit]
There are three primary types of modulation: amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation.
Amplitude Modulation[edit]
In amplitude modulation (AM), the amplitude of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the waveform being sent. This waveform may correspond to sounds to be reproduced by a loudspeaker, or the light intensity of television pixels.
Frequency Modulation[edit]
Frequency modulation (FM) is a method of impressing data onto an alternating-current (AC) wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. This technique is commonly used in broadcasting, especially in the FM radio band.
Phase Modulation[edit]
Phase modulation (PM) is a modulation pattern that encodes information as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. PM is used in digital music synthesis and telecommunications systems.
Applications of Modulation[edit]
Modulation is used in numerous fields such as telecommunications, broadcasting, and data communication. It is also used in systems such as Ethernet to encode data onto a carrier signal.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
Modulation[edit]
-
Modulation categorization
-
AM and FM modulation
-
Waterfall AM
-
Waterfall FM
-
Baud rate