Biceps tendon rupture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[[Category:Injuries]] | [[Category:Injuries]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Biceps_tendon_rupture == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Biceps_brachii_muscle06.png|Biceps brachii muscle | |||
File:BicepstendonRupture_-_Copy.jpg|Biceps tendon rupture | |||
File:Dist._bizepssehnenruptur.jpg|Distal biceps tendon rupture | |||
File:Proximal_rupture_repair.png|Proximal rupture repair | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:49, 20 February 2025
Biceps Tendon Rupture
A biceps tendon rupture involves the tearing or breaking of the biceps tendon, which connects the biceps muscle to bones in the shoulder and elbow. This condition can lead to significant loss of strength and mobility in the affected arm. Biceps tendon ruptures can occur at either the proximal end (near the shoulder) or the distal end (near the elbow), with proximal ruptures being more common.
Causes[edit]
The rupture of the biceps tendon is often the result of a sudden injury or excessive strain. In the case of proximal ruptures, degenerative changes due to aging or repetitive overhead activities can weaken the tendon over time. Distal ruptures are less common and are usually associated with heavy lifting or forceful bending of the elbow.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of a biceps tendon rupture include:
- A sudden, sharp pain in the upper arm or at the elbow, depending on the location of the rupture
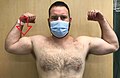
- Swelling, bruising, or a visible bulging (often referred to as a "Popeye" muscle) in the arm
- Weakness in bending the elbow or rotating the arm
- A snapping sound or sensation at the time of injury
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a biceps tendon rupture typically involves a physical examination and the patient's medical history. Imaging tests, such as MRI or ultrasound, may be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the rupture.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment options for a biceps tendon rupture vary depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's lifestyle. Non-surgical treatments, such as rest, ice, and physical therapy, may be recommended for less severe injuries. Surgical repair may be necessary for complete ruptures or for patients who require full strength and functionality of the arm.
Surgical Options[edit]
Surgical options for repairing a biceps tendon rupture include:
- Tenodesis, where the tendon is reattached to the bone
- Tendon transfer, where another tendon is used to replace the damaged biceps tendon
Recovery[edit]
Recovery from a biceps tendon rupture can take several months. Physical therapy is an important part of the recovery process, helping to restore strength and flexibility to the affected arm.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures for a biceps tendon rupture include:
- Regular strength training and stretching exercises to maintain muscle and tendon health
- Avoiding sudden increases in the intensity or volume of physical activities
- Using proper techniques when lifting heavy objects
Biceps_tendon_rupture[edit]
-
Biceps brachii muscle
-
Biceps tendon rupture
-
Distal biceps tendon rupture
-
Proximal rupture repair