Clay-shoveler fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic injuries]] | [[Category:Orthopedic injuries]] | ||
[[Category:Spinal disorders]] | [[Category:Spinal disorders]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:C7_animation_small.gif|Clay-shoveler fracture | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 21:37, 20 February 2025
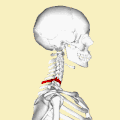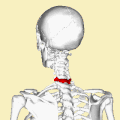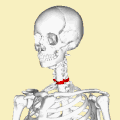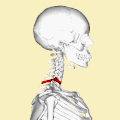
A Clay-shoveler's fracture is a type of spinal fracture that occurs in the cervical vertebrae, specifically affecting the spinous process of the lower cervical vertebrae, most commonly at the C7 level. This injury is typically caused by sudden muscle contraction or direct trauma to the spine.
Etiology
The name "Clay-shoveler's fracture" originates from the early 20th century when Australian clay miners were noted to suffer from this injury due to the repetitive and forceful shoveling of clay. The sudden downward force exerted on the spine during shoveling could lead to an avulsion fracture of the spinous process.
Pathophysiology
The fracture occurs when the trapezius muscle and other muscles attached to the spinous process contract forcefully, causing a piece of the bone to break off. This is an avulsion-type fracture, where the muscle pulls a fragment of bone away from the main structure.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with a Clay-shoveler's fracture typically present with:
- Localized pain at the site of the fracture, often exacerbated by movement.
- Swelling and tenderness over the affected spinous process.
- Limited range of motion in the neck.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is primarily made through radiography. A lateral X-ray of the cervical spine will typically show the fracture of the spinous process. In some cases, a CT scan may be used for further evaluation.
Treatment
Treatment for a Clay-shoveler's fracture is usually conservative, as the injury is considered stable. Management includes:
- Rest and avoidance of activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications for pain relief.
- Physical therapy to restore range of motion and strengthen neck muscles.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with a Clay-shoveler's fracture is generally excellent. Most patients recover fully with conservative treatment, and the fracture typically heals without complications.
Related pages
-
Clay-shoveler fracture