Birch triterpenes: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
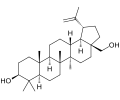
File:Betulin.svg|Betulin | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:34, 20 February 2025
Birch Triterpenes are a group of chemical compounds found in the bark of birch trees, specifically the Betula species. They are part of a larger class of compounds known as triterpenes, which are widely distributed in the plant kingdom. Birch triterpenes have been studied for their potential medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anti-cancer activities.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Birch triterpenes are composed of six isoprene units and have the molecular formula C30H48. They are characterized by a four-ring structure, with variations in the side chains and functional groups that differentiate the various types of triterpenes found in birch bark. The most common birch triterpenes include betulin, betulinic acid, and lupeol.
Medicinal Properties[edit]
Birch triterpenes have been the subject of numerous pharmacological studies due to their potential medicinal properties.
Anti-Inflammatory[edit]
Birch triterpenes, particularly betulin and betulinic acid, have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. They inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduce the activity of enzymes involved in the inflammatory response.
Anti-Viral[edit]
Some studies have suggested that birch triterpenes may have anti-viral activity. Betulinic acid, in particular, has been shown to inhibit the replication of certain viruses, including HIV.
Anti-Cancer[edit]
Birch triterpenes have also been studied for their potential anti-cancer properties. Both betulin and betulinic acid have been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth in animal models.
Extraction and Use[edit]
Birch triterpenes can be extracted from the bark of birch trees using various methods, including solvent extraction and supercritical fluid extraction. They can be used in the formulation of pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, and cosmetics.
Safety and Toxicity[edit]
While birch triterpenes have been shown to have potential medicinal properties, their safety and toxicity have not been fully evaluated. Some studies have suggested that they may have low toxicity, but further research is needed.
See Also[edit]
-
Betulin