HHCP-O-acetate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
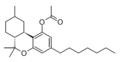
File:HHCPO structure.png|HHCP-O-acetate | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:39, 20 February 2025
HHCP-O-acetate is a chemical compound that is often used in the field of pharmacology. It is a derivative of the parent compound HHCP (Hexahydrocannabinol), which is a synthetic cannabinoid. HHCP-O-acetate is created through the process of acetylation, where an acetyl group is introduced into the HHCP molecule.
Chemical Structure[edit]
The chemical structure of HHCP-O-acetate is similar to that of its parent compound, HHCP. The primary difference is the addition of an acetyl group, which is represented by the formula -C(O)CH3. This acetyl group is attached to the oxygen atom in the HHCP molecule, resulting in the formation of HHCP-O-acetate.
Pharmacological Properties[edit]
As a derivative of HHCP, HHCP-O-acetate shares many of the same pharmacological properties. It is believed to act on the cannabinoid receptors in the body, specifically the CB1 and CB2 receptors. These receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in a variety of physiological processes including pain sensation, mood, and memory.
Medical Uses[edit]
While the medical uses of HHCP-O-acetate are still being researched, it is believed that it may have potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, and epilepsy. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of this compound.
Safety and Side Effects[edit]
Like other cannabinoids, HHCP-O-acetate may have a range of side effects. These can include dizziness, dry mouth, and changes in appetite. It is also important to note that the safety profile of HHCP-O-acetate has not been fully established, and it should be used with caution until more is known about its effects.
See Also[edit]
-
HHCP-O-acetate