Shoulder replacement: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
[[Category:Arthritis]] | [[Category:Arthritis]] | ||
[[Category:Physical Therapy]] | [[Category:Physical Therapy]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
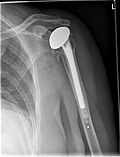
File:Shoulderprotesis.jpg|Shoulder replacement | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:37, 20 February 2025
Shoulder Replacement is a surgical procedure where the damaged parts of the shoulder are removed and replaced with artificial components, referred to as a prosthesis. The treatment is conducted to relieve pain and improve mobility.
Indications[edit]
Shoulder Replacement is typically recommended for patients suffering from severe forms of arthritis or those who have sustained significant shoulder injuries. The primary goal of the procedure is to relieve pain, with secondary goals including improving motion, strength, and function.
Procedure[edit]
During a Shoulder Replacement procedure, the damaged parts of the shoulder, including the humerus (upper arm bone) and the scapula (shoulder blade), are replaced with artificial components. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Types of Shoulder Replacement[edit]
There are two main types of Shoulder Replacement surgeries: Total Shoulder Replacement and Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement.
Total Shoulder Replacement[edit]
In a Total Shoulder Replacement, the damaged parts of the shoulder are removed and replaced with artificial components. The top of the humerus is replaced with a metal ball and stem, while the shoulder socket is replaced with a plastic socket.
Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement[edit]
In a Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement, the socket and metal ball are switched. This means the metal ball is attached to the shoulder bone and the plastic socket is attached to the upper arm bone. This allows the patient to use the deltoid muscle instead of the torn rotator cuff to lift the arm.
Risks and Complications[edit]
As with any surgery, there are risks associated with Shoulder Replacement. These may include infection, nerve injury, blood clots, and complications from anesthesia.
Recovery[edit]
Recovery from a Shoulder Replacement surgery typically involves physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility in the shoulder. The duration of recovery can vary depending on the individual patient's health and the type of surgery performed.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />