Sentinel lymph node: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Swollen Lymph Nodes.jpg|Sentinel lymph node | |||
File:Sentinel lymph node (axilla).jpg|Sentinel lymph node | |||
File:Breast carcinoma in a lymph node.jpg|Sentinel lymph node | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:24, 20 February 2025
Sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes reached by metastasizing cancer cells from a primary tumor. The spread of metastasis may be predicted by the sentinel node concept, based on the assumption that the progression of metastatic disease is orderly and predictable, moving from the primary tumor to the sentinel node, then to the next echelon nodes.
Overview[edit]
The sentinel lymph node is the first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancer (invasive), the sentinel node is the first node that metastatic cells will reach. Therefore, a pathologist can determine whether cancer has reached the lymph nodes by examining only the sentinel nodes. If the sentinel nodes are free of cancer, then it is assumed that the cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
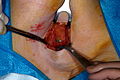
Sentinel lymph node biopsy[edit]
A Sentinel lymph node biopsy is a surgical procedure used to determine if cancer has spread beyond a primary tumor into your lymphatic system. It's used most commonly in evaluating breast cancer and melanoma. The sentinel nodes are the first few lymph nodes into which a tumor drains. Sentinel node biopsy involves injecting a tracer material that helps the surgeon locate the sentinel nodes during surgery. The sentinel nodes are removed and tested for cancer.
Clinical significance[edit]
If the sentinel lymph node does not contain cancer cells (node negative), then the cancer has not likely spread to other lymph nodes or other places in the body. If the sentinel lymph node does contain cancer cells (node positive), then the cancer has spread to the lymphatic system. This can help guide decisions about treatment.