Mirex: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{Public-health-stub}} | {{Public-health-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Mirex.svg|Mirex | |||
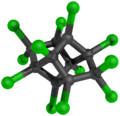
File:Mirex 3D.png|Mirex | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:14, 20 February 2025
Mirex is a synthetic, colorless, crystalline solid that is odorless and tasteless. It is a chlorinated hydrocarbon that was commercially introduced in the late 1950s by the chemical industry for use as an insecticide and later as a fire retardant in plastics, rubber, and electrical goods.
History[edit]
Mirex was first synthesized in 1955. It was primarily used as an insecticide in the southern United States from 1962 to 1978 to combat the fire ant. It was also used as a fire retardant in plastics, rubber, and electrical goods. However, due to its environmental persistence and potential for bioaccumulation, the use of Mirex was banned in the United States in 1978 by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Chemical Properties[edit]
Mirex is a stable, white, crystalline solid with a melting point of 485°C. It is virtually insoluble in water but is soluble in fats and oils. Mirex is resistant to both chemical degradation and biodegradation, which makes it highly persistent in the environment.
Health Effects[edit]
Exposure to Mirex can occur through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. It has been shown to have both acute and chronic effects on human health. Acute exposure can lead to skin irritation, while chronic exposure can result in damage to the skin, liver, and nervous system. Mirex is also a potential human carcinogen.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Mirex is highly persistent in the environment due to its resistance to degradation. It can bioaccumulate in aquatic and terrestrial organisms, leading to long-term exposure. Mirex can also undergo long-range atmospheric transport, leading to global distribution.
Regulation[edit]
The production and use of Mirex have been banned in many countries due to its environmental and health effects. In the United States, the EPA banned the use of Mirex in 1978. Internationally, Mirex is listed as a Persistent Organic Pollutant under the Stockholm Convention.
This article is a Chemical compound-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
This insecticide-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
This environmental science related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.

This article is a toxicology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
This public health related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Mirex
-
Mirex