Substituted tryptamine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{Psychoactive drug-stub}} | {{Psychoactive drug-stub}} | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Tryptamine rests General Formula V.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:Tryptamine structure.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:Tryptamine structure.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:NMT structure.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:2-Hydroxy-NMT.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:5-MeO-NMT.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:Serotonin-2D-skeletal.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:Norbufotenine.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:Bufotenin2DACS.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:Bufotenidine.png|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:Melatonin.svg|Substituted tryptamine | |||
File:N-Acetylserotonin.png|Substituted tryptamine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:10, 20 February 2025
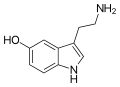
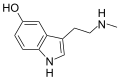
Substituted tryptamine refers to a class of molecules that are structurally derived from the tryptamine molecule. The tryptamine structure is the backbone for a group of compounds termed collectively as substituted tryptamines. This class of drug contains a broad range of psychedelic, stimulant, and antidepressant effects.
Structure and Function[edit]
Substituted tryptamines have the same core structure as tryptamine, but with additional substituents attached to the molecule. The structure of tryptamine is a combination of an indole ring and an ethylamine side chain. The substitutions can occur at various positions on the tryptamine molecule, leading to a wide variety of compounds with different effects.
Pharmacology[edit]
The pharmacology of substituted tryptamines is complex and varies depending on the specific compound. Many substituted tryptamines are serotonin agonists, meaning they bind to and activate serotonin receptors in the brain. This can lead to a range of effects, including hallucinations, altered perception, and mood elevation.
Examples of Substituted Tryptamines[edit]
There are many examples of substituted tryptamines, including both naturally occurring compounds and synthetic drugs. Some examples include:
- Psilocybin: A naturally occurring psychedelic compound found in certain species of mushrooms.
- DMT (Dimethyltryptamine): A powerful psychedelic compound found in a variety of plant species, and in trace amounts in the human body.
- AMT (Alpha-Methyltryptamine): A synthetic compound with stimulant, psychedelic, and entactogenic effects.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of substituted tryptamines varies greatly by country and by specific compound. In many countries, including the United States, many substituted tryptamines are classified as controlled substances, making their manufacture, sale, and possession illegal.
See Also[edit]
This article is a Psychoactive drug-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine
-
Substituted tryptamine