Pharmacology of bicalutamide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[Category:Prostate cancer drugs]] | [[Category:Prostate cancer drugs]] | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Bicalutamide.svg|Bicalutamide | |||
File:W741L AR LBD-R-bicalutamide complex.png|W741L AR LBD-R-bicalutamide complex | |||
File:Androgen receptor antagonistic potency of spironolactone, cyproterone acetate, and flutamide in male rats.png|Androgen receptor antagonistic potency of spironolactone, cyproterone acetate, and flutamide in male rats | |||
File:Median prostate-specific antigen reduction across bicalutamide dosages and with castration.png|Median prostate-specific antigen reduction across bicalutamide dosages and with castration | |||
File:Bicalutamide and the hypothalamic-pituitary-glandular axes.png|Bicalutamide and the hypothalamic-pituitary-glandular axes | |||
File:Testosterone levels with 10, 30, and 50 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men.png|Testosterone levels with 10, 30, and 50 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men | |||
File:Testosterone levels with 10 to 200 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men.png|Testosterone levels with 10 to 200 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men | |||
File:Estradiol levels with 10, 30, and 50 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men.png|Estradiol levels with 10, 30, and 50 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men | |||
File:Estradiol levels with 10 to 200 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men.png|Estradiol levels with 10 to 200 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men | |||
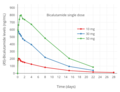
File:(R)-Bicalutamide levels with a single 5 to 80 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men.png|(R)-Bicalutamide levels with a single 5 to 80 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men | |||
File:Bicalutamide levels after a single 50 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men.png|Bicalutamide levels after a single 50 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men | |||
File:Bicalutamide levels after a single 10, 30, or 50 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men.png|Bicalutamide levels after a single 10, 30, or 50 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:52, 20 February 2025
Bicalutamide is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) used primarily in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is a pure androgen receptor (AR) antagonist that prevents androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from stimulating the AR.
Pharmacodynamics[edit]
Bicalutamide acts as a pure antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR). Unlike earlier antiandrogens such as flutamide and nilutamide, bicalutamide does not induce DNA damage, and is thus classified as a "pure" antiandrogen. It competes with testosterone and its powerful metabolite, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) for binding to ARs in tissues like the prostate gland. By doing so, it prevents them from stimulating the AR.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Bicalutamide is well-absorbed when taken by mouth and can be taken with or without food. It is highly protein-bound and has a very long elimination half-life, allowing for once-daily dosing. Bicalutamide is extensively metabolized in the liver via hydroxylation and glucuronidation. Its metabolites are eliminated in both urine and feces.
Clinical use[edit]
Bicalutamide is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is also used as an adjunct to surgical castration in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. In addition, it has been used off-label for the treatment of other androgen-dependent conditions, including hirsutism, acne, and androgenic alopecia.
Side effects[edit]
The most common side effects of bicalutamide are hot flashes, breast tenderness and enlargement, and sexual dysfunction. Less common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, liver function test abnormalities, and an increased risk of heart failure.
See also[edit]
-
Bicalutamide
-
W741L AR LBD-R-bicalutamide complex
-
Androgen receptor antagonistic potency of spironolactone, cyproterone acetate, and flutamide in male rats
-
Median prostate-specific antigen reduction across bicalutamide dosages and with castration
-
Bicalutamide and the hypothalamic-pituitary-glandular axes
-
Testosterone levels with 10, 30, and 50 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men
-
Testosterone levels with 10 to 200 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men
-
Estradiol levels with 10, 30, and 50 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men
-
Estradiol levels with 10 to 200 mg per day bicalutamide monotherapy in men
-
(R)-Bicalutamide levels with a single 5 to 80 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men
-
Bicalutamide levels after a single 50 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men
-
Bicalutamide levels after a single 10, 30, or 50 mg oral dose of bicalutamide in men