Mitral regurgitation: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Mitral_Regurgitation_scheme1.png|Mitral regurgitation schematic | |||
File:Phonocardiograms_from_normal_and_abnormal_heart_sounds.svg|Phonocardiograms from normal and abnormal heart sounds | |||
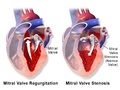
File:Blausen_0645_MitralValve_RegurgitationvsStenosis.png|Mitral valve regurgitation vs stenosis | |||
File:MI_Schema_leicht_Kopie.png|Mitral regurgitation schematic | |||
File:Mitralinsuff_TEE.jpg|Mitral regurgitation TEE | |||
File:Mitral_regurgitation_echo_4chamber.jpg|Mitral regurgitation echo 4 chamber | |||
File:Mitral_regurgitation_echo_4chamber_description.png|Mitral regurgitation echo 4 chamber description | |||
File:Doppler_mitral_valve.gif|Doppler mitral valve | |||
File:The_PISA_Method_for_Quantification_of_Mitral_Regurgitation.svg|The PISA method for quantification of mitral regurgitation | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:19, 18 February 2025
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency, is a condition in which the mitral valve in the heart does not close properly, allowing blood to flow backward into the left atrium when the left ventricle contracts. This can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations.
Causes
Mitral regurgitation can be caused by a variety of conditions, including mitral valve prolapse, rheumatic heart disease, endocarditis, and myocardial infarction. It can also be a complication of cardiac surgery.
Symptoms
The symptoms of mitral regurgitation can vary depending on the severity of the condition. They may include shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, chest pain, and edema (swelling) in the legs and ankles.
Diagnosis
Mitral regurgitation is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as echocardiography and cardiac MRI.
Treatment
The treatment for mitral regurgitation depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. It may include medication, surgery, or catheter procedures.
See also
|
|
|
-
Mitral regurgitation schematic
-
Phonocardiograms from normal and abnormal heart sounds
-
Mitral valve regurgitation vs stenosis
-
Mitral regurgitation schematic
-
Mitral regurgitation TEE
-
Mitral regurgitation echo 4 chamber
-
Mitral regurgitation echo 4 chamber description
-
Doppler mitral valve
-
The PISA method for quantification of mitral regurgitation