Intraductal papilloma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Intraductal_papilloma_histopathology_(3)_p63.JPG|Intraductal papilloma histopathology (p63 stain) | |||
File:Intraductal_papilloma_histopathology_(1).jpg|Intraductal papilloma histopathology | |||
File:Intraductal_papilloma_histopathology_(2)_smooth_muscle_actin.JPG|Intraductal papilloma histopathology (smooth muscle actin stain) | |||
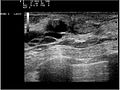
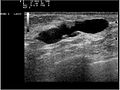
File:Ultrasound_12070I26_intraductal_papilloma_nevit.jpg|Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma | |||
File:Ultrasound_12070I33_intraductal_papilloma_nevit.jpg|Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma | |||
File:Ultrasound_12070I40_intraductal_papilloma_nevit.jpg|Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma | |||
File:Ultrasound_12070I6_intraductal_papilloma_nevit.jpg|Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma | |||
File:Ultrasound_12070I25_intraductal_papilloma_nevit.jpg|Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma | |||
File:Ultrasound_12070I12_intraductal_papilloma_nevit.jpg|Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:12, 18 February 2025
Intraductal papilloma is a small, benign tumor that forms in a milk duct in the breast. These tumors are made of gland and fibrous tissue as well as blood vessels. They most commonly occur in women aged 35-55 years.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of intraductal papilloma is nipple discharge, which is often clear or bloody. Other symptoms may include a lump in the breast or nipple and nipple inversion or retraction. In some cases, intraductal papilloma may cause no symptoms and may be discovered during a routine mammogram.
Causes
The exact cause of intraductal papilloma is not known. However, it is believed to be related to changes in hormone levels, as these tumors are more common in women who are nearing menopause.
Diagnosis
Intraductal papilloma is usually diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests such as mammography or ultrasound, and biopsy. The biopsy can be performed using fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, or surgical biopsy.
Treatment
The treatment for intraductal papilloma usually involves surgical removal of the tumor. In some cases, the entire affected milk duct may be removed. If the biopsy shows that the papilloma has atypical cells or is associated with a high risk of breast cancer, additional treatment such as radiation therapy or hormone therapy may be recommended.
Prognosis
The prognosis for intraductal papilloma is generally good. However, these tumors can sometimes be associated with a slightly increased risk of developing breast cancer.
See also:
|
|
|
-
Intraductal papilloma histopathology (p63 stain)
-
Intraductal papilloma histopathology
-
Intraductal papilloma histopathology (smooth muscle actin stain)
-
Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma
-
Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma
-
Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma
-
Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma
-
Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma
-
Ultrasound of intraductal papilloma