Boronic acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Category:Organoboron compounds]] | [[Category:Organoboron compounds]] | ||
{{chemistry-stub}} | {{chemistry-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Boronic-acid-2D.png|Boronic acid | |||
File:Phenylboronic_acid.png|Phenylboronic acid | |||
File:2-Thienylboronic_acid.svg|2-Thienylboronic acid | |||
File:Methylboronic_acid.svg|Methylboronic acid | |||
File:cis-Propenylboronic_acid.svg|cis-Propenylboronic acid | |||
File:trans-Propenylboronic_acid.svg|trans-Propenylboronic acid | |||
File:Boronic-acid-2D.png|Boronic acid | |||
File:Boronate-ester-2D.png|Boronate ester | |||
File:Allylboronic_acid_pinacol_ester.svg|Allylboronic acid pinacol ester | |||
File:Phenylboronic_acid_trimethylene_glycol_ester.svg|Phenylboronic acid trimethylene glycol ester | |||
File:Diisopropoxymethylborane.svg|Diisopropoxymethylborane | |||
File:ChanLamCoupling.png|Chan-Lam coupling | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:09, 18 February 2025

Boronic acid refers to any compound containing a boronic group, which is composed of a boron atom connected to three hydrogens and one carbon atom, denoted as BR2OH, where R can be any alkyl or aryl group. Boronic acids are a versatile class of compounds in organic chemistry and are particularly important in the field of medicinal chemistry and material science.
Boronic acids are known for their unique reactivity, especially their ability to form reversible covalent bonds with diols, including sugars, and amino acids. This property makes them invaluable tools in the synthesis of complex organic molecules, including pharmaceuticals, and in the development of sensors and catalysts.
Synthesis
The synthesis of boronic acids typically involves the reaction of organoboranes with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or the direct borylation of organic halides or triflates using a boron source, such as diborane (B2H6) or bis(pinacolato)diboron ([B2(pin)2]). These methods allow for the introduction of various functional groups to the boron atom, enabling the synthesis of a wide range of boronic acid derivatives.
Applications
Suzuki Coupling
One of the most significant applications of boronic acids is in the Suzuki coupling reaction, a cross-coupling reaction that forms carbon-carbon bonds between a boronic acid and a halide, catalyzed by a palladium (Pd) catalyst. This reaction is widely used in the synthesis of complex organic molecules, including natural products, pharmaceuticals, and polymers.
Sensing and Detection
Boronic acids are also used in the development of chemical sensors for the detection of sugars and other diol-containing compounds. Their ability to form reversible covalent bonds with diols is exploited in the design of sensors that can detect glucose, which is particularly important in the management of diabetes.
Drug Design
In drug design, boronic acids have been utilized as key components in the development of proteasome inhibitors, such as Bortezomib, a drug used in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Their unique reactivity allows for the selective targeting of biological molecules, making them valuable tools in medicinal chemistry.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
While boronic acids are generally considered to be less toxic than other boron-containing compounds, such as boranes, they should still be handled with care. Proper safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and adequate ventilation, are recommended when working with these compounds. Environmental considerations should also be taken into account, as some boronic acids may pose risks to aquatic life.
-
Boronic acid
-
Phenylboronic acid
-
2-Thienylboronic acid
-
Methylboronic acid
-
cis-Propenylboronic acid
-
trans-Propenylboronic acid
-
Boronic acid
-
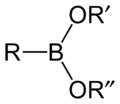
Boronate ester
-
Allylboronic acid pinacol ester
-
Phenylboronic acid trimethylene glycol ester
-
Diisopropoxymethylborane
-
Chan-Lam coupling