Agkistrodon piscivorus: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
[[Category:Reptiles of the United States]] | [[Category:Reptiles of the United States]] | ||
[[Category:Venomous snakes]] | [[Category:Venomous snakes]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Agkistrodon_piscivorus_piscivorus_CDC.png|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Cottonmouth_(Agkistrodon_piscivorus).jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Juvenile_Cottonmouth.jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
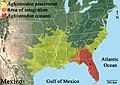
File:Geographic_distribution_of_the_two_species_of_cottonmouth,_Agkistrodon_piscivorus_and_Agkistrodon_conanti.jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Big_cypress.jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Cottonmouth_Snake,_Gaping.jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Watersnake_cottonmouth_tennessee.png|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Nerodia-sipedon-004.jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Cottonmouth_(aka_water_moccasin)_(Agkistrodon_piscivorus)_(6307259102).jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Tiki3_cropped.jpg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
File:Central_fusion_and_terminal_fusion_automixis.svg|Agkistrodon piscivorus | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:03, 18 February 2025
Agkistrodon piscivorus[edit]

Agkistrodon piscivorus, commonly known as the cottonmouth or water moccasin, is a venomous snake species found in the southeastern United States. It is a member of the Viperidae family and is known for its potent venom and distinctive threat display.
Description[edit]
The cottonmouth is a large, heavy-bodied snake with a broad head and a distinctive dark line through each eye. Adults typically range from 50 to 135 cm in length, with some individuals reaching up to 180 cm. The coloration of the cottonmouth can vary, but it is generally dark brown or black with lighter crossbands. Juveniles are more brightly colored with reddish-brown crossbands and a yellow-tipped tail.

Behavior[edit]
Cottonmouths are semi-aquatic and are often found near bodies of water such as swamps, marshes, and slow-moving streams. They are known for their defensive behavior, which includes opening their mouths wide to display the white interior, hence the name "cottonmouth." This display is often accompanied by a loud hiss.
Diet[edit]
The diet of Agkistrodon piscivorus primarily consists of fish and amphibians, but they are opportunistic feeders and will consume small mammals, birds, and other reptiles when available.
Reproduction[edit]
Cottonmouths are ovoviviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. Mating typically occurs in the spring, and females give birth to 1-16 young in late summer or early fall.
Distribution and Habitat[edit]

Agkistrodon piscivorus is found throughout the southeastern United States, from Virginia to Florida and west to Texas and Oklahoma. They inhabit a variety of wetland habitats, including swamps, marshes, and the edges of ponds and lakes.
Venom[edit]
The venom of the cottonmouth is hemotoxic, causing tissue destruction and disruption of blood clotting. Bites can be serious and require medical attention, but fatalities are rare with prompt treatment.
Conservation[edit]
The cottonmouth is not currently listed as threatened or endangered. However, habitat destruction and human persecution pose threats to local populations.
Related pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Cottonmouth in natural habitat
-
Habitat of the cottonmouth
-
Cottonmouth displaying its white mouth
-
Cottonmouth in Tennessee
-
Similar species: Northern watersnake
-
Cottonmouth in defensive posture
-
Cottonmouth in captivity
-
Diagram of automixis, a form of reproduction
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus
-
Agkistrodon piscivorus