Optic tract: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray773.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Optic_tract.JPG|Optic_tract | |||
File:Hippocampus_(brain).jpg|Optic_tract | |||
File:lateral_geniculate_nucleus.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Gray689.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Gray718.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Gray719.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Gray722.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Gray724.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Gray730.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Gray745.png|Optic_tract | |||
File:Human_brainstem_anterior_view_2_description.JPG|Optic_tract | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:52, 18 February 2025
Optic Tract
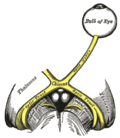
The Optic Tract is an essential part of the visual system in the human body. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays visual information from the optic chiasm to the lateral geniculate nucleus, superior colliculus, and other destinations.
Anatomy
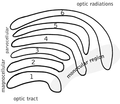
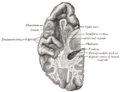
The optic tract is a bundle of nerve fibers that extends from the optic chiasm to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus. It carries visual information from the retina to the brain. The optic tract wraps around the midbrain to reach the lateral geniculate nucleus, passing through the temporal lobe and the parietal lobe of the brain.
Function
The primary function of the optic tract is to transmit visual information from the retina to the brain. This information includes details about color, brightness, and contrast, as well as motion and other visual cues. The optic tract also plays a role in the pupillary light reflex, a reflex that adjusts the size of the pupil in response to changes in light intensity.
Clinical Significance
Damage to the optic tract can result in a variety of visual impairments, including hemianopsia, a condition characterized by loss of vision or blindness in half the visual field. Other potential conditions include akinetopsia, the inability to perceive motion, and achromatopsia, the inability to perceive color.
See Also
References
<references />