Membrane bioreactor: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[Category:Environmental engineering]] | [[Category:Environmental engineering]] | ||
{{environment-stub}} | {{environment-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:MBR_Schematic.jpg|Schematic of a Membrane Bioreactor | |||
File:MBRvsASP_Schematic.jpg|Comparison of MBR and Activated Sludge Process | |||
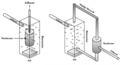
File:MBR_Setups.png|Different Setups of Membrane Bioreactors | |||
File:Wastewater_UF_membrane_system,_Aquabio.jpg|Wastewater Ultrafiltration Membrane System by Aquabio | |||
File:ZeeWeed_500_ultrafiltration_module_at_a_NEWater_plant.jpg|ZeeWeed 500 Ultrafiltration Module at a NEWater Plant | |||
File:MBR_FiltrationFactors.jpg|Factors Affecting MBR Filtration | |||
File:MBR_Cleaning.jpg|Cleaning Process in Membrane Bioreactors | |||
File:MBR_NutrientRemoval.jpg|Nutrient Removal in Membrane Bioreactors | |||
File:MBR-Mixing_RTD-and-CFD.jpg|Mixing, RTD, and CFD in Membrane Bioreactors | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:39, 18 February 2025
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) is an advanced technology used in wastewater treatment and water purification. It combines conventional biological treatment processes with membrane filtration to remove organic and inorganic substances from water. This article provides an overview of the membrane bioreactor process, its applications, advantages, and challenges.
Overview[edit]
A Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) is a sophisticated system that integrates a membrane process like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a biological wastewater treatment process, typically a suspended growth bioreactor. The integration of these processes into a single system allows for efficient removal of pollutants from wastewater, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from municipal to industrial wastewater treatment.
Components[edit]
The MBR system consists of two main components:
- Biological Reactor: This is where the biological degradation of organic matter takes place. Microorganisms, including bacteria and protozoa, consume organic pollutants, converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass.
- Membrane Module: This component is responsible for the physical separation of treated water from suspended solids, microorganisms, and some large molecular weight solutes. The membrane module can operate in various configurations, such as submerged or side-stream.
Operation[edit]
In an MBR system, wastewater enters the biological reactor, where microorganisms degrade organic pollutants. The mixed liquor then flows into the membrane module, where treated water permeates through the membrane fibers, and the concentrated mixed liquor recirculates back to the biological reactor. The process operates continuously, with the membrane providing a barrier that allows for the retention of biomass and the production of high-quality effluent.
Applications[edit]
MBR technology is used in various applications, including:
- Municipal wastewater treatment
- Industrial wastewater treatment
- Water reuse and recycling
- Pretreatment for reverse osmosis systems
Advantages[edit]
The main advantages of MBR systems include:
- High-quality effluent suitable for reuse
- Compact footprint due to the integration of processes
- Reduced sludge production compared to conventional systems
- Ability to operate at higher mixed liquor suspended solids concentrations
Challenges[edit]
Despite its benefits, MBR technology faces several challenges:
- Membrane fouling, which can reduce system efficiency and increase operational costs
- Higher energy consumption compared to conventional treatment processes
- Capital and operational costs can be significant
Conclusion[edit]
Membrane Bioreactor technology represents a significant advancement in wastewater treatment, offering numerous benefits over traditional methods. However, challenges such as membrane fouling and high costs need to be addressed to enhance its applicability and efficiency. As research continues and technology advances, MBR systems are expected to become more accessible and cost-effective, playing a crucial role in sustainable water management practices.

This article is a environment-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Schematic of a Membrane Bioreactor
-
Comparison of MBR and Activated Sludge Process
-
Different Setups of Membrane Bioreactors
-
Wastewater Ultrafiltration Membrane System by Aquabio
-
ZeeWeed 500 Ultrafiltration Module at a NEWater Plant
-
Factors Affecting MBR Filtration
-
Cleaning Process in Membrane Bioreactors
-
Nutrient Removal in Membrane Bioreactors
-
Mixing, RTD, and CFD in Membrane Bioreactors