Casein kinase 1: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[Category:Signal transduction]] | [[Category:Signal transduction]] | ||
[[Category:Circadian rhythm]] | [[Category:Circadian rhythm]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
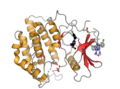
File:Human_casein_kinase_1_alpha_PDB_6GZD.png|Human casein kinase 1 alpha structure | |||
File:Human_casein_kinase_1_gamma_1_PDB_2CMW.png|Human casein kinase 1 gamma 1 structure | |||
File:Human_casein_kinase_1_gamma_2_PDB_2C47.png|Human casein kinase 1 gamma 2 structure | |||
File:Human_casein_kinase_1_gamma_3_PDB_2CHL.png|Human casein kinase 1 gamma 3 structure | |||
File:Human_casein_kinase_1_delta_PDB_4TWC.png|Human casein kinase 1 delta structure | |||
File:Human_casein_kinase_1_epsilon_PDB_4HNI.png|Human casein kinase 1 epsilon structure | |||
File:CC-BY_icon.svg|Casein_kinase_1 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 18 February 2025
Casein Kinase 1[edit]
Casein kinase 1 (CK1) is a family of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that are involved in various cellular processes, including the regulation of the circadian rhythm, cell division, and signal transduction pathways. CK1 enzymes are highly conserved across eukaryotic species and play critical roles in the phosphorylation of key proteins involved in these processes.
Structure and Isoforms[edit]
CK1 is a monomeric enzyme that consists of a catalytic domain and a regulatory domain. The CK1 family includes several isoforms, such as CK1α, CK1β, CK1γ, CK1δ, and CK1ε, each encoded by different genes and exhibiting distinct but overlapping substrate specificities and cellular functions.
Function[edit]
CK1 enzymes are involved in the phosphorylation of a wide range of substrates, including:
- Circadian rhythm proteins such as PER and CRY, which are crucial for maintaining the body's internal clock.
- Wnt signaling pathway components, where CK1 phosphorylates β-catenin, influencing cell fate decisions.
- DNA repair proteins, contributing to the maintenance of genomic stability.
CK1 activity is regulated by various mechanisms, including autophosphorylation, interaction with other proteins, and cellular localization.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Dysregulation of CK1 activity has been implicated in several diseases, including:
- Cancer, where altered CK1 activity can affect cell proliferation and apoptosis.
- Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, where CK1 is involved in the phosphorylation of tau protein.
- Sleep disorders, due to its role in circadian rhythm regulation.
Research and Therapeutic Potential[edit]
CK1 inhibitors are being explored as potential therapeutic agents for treating various conditions, including cancer and sleep disorders. Understanding the specific roles and regulation of different CK1 isoforms is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
Also see[edit]
- Protein kinase
- Signal transduction
- Circadian rhythm
- Wnt signaling pathway
- Serine/threonine-specific protein kinase
-
Human casein kinase 1 alpha structure
-
Human casein kinase 1 gamma 1 structure
-
Human casein kinase 1 gamma 2 structure
-
Human casein kinase 1 gamma 3 structure
-
Human casein kinase 1 delta structure
-
Human casein kinase 1 epsilon structure
-
Casein_kinase_1