Dipole: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category:Antennas]] | [[Category:Antennas]] | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
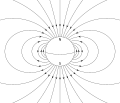
File:VFPt_Dipole_field.svg|Dipole field | |||
File:DipoleContourPoint.svg|Dipole contour point | |||
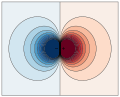
File:VFPt_dipole_electric.svg|Electric dipole | |||
File:VFPt_dipole_magnetic2.svg|Magnetic dipole | |||
File:VFPt_dipole_point.svg|Dipole point | |||
File:Carbon-dioxide-2D-dimensions.svg|Carbon dioxide dimensions | |||
File:H2O_2D_labelled.svg|Water molecule labelled | |||
File:Ozone-resonance-Lewis-2D.svg|Ozone resonance Lewis structure | |||
File:Electric_dipole_radiation.gif|Electric dipole radiation | |||
File:dipole.gif|Dipole | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:34, 18 February 2025
Dipole is a term used in physics and chemistry to describe a pair of equal and oppositely charged or magnetized poles separated by a distance. A simple example of a dipole is a pair of electric charges or magnetic poles of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some (usually small) distance.
Physics[edit]
In physics, a dipole can refer to various quantities that can be defined as a vector from one pole to the other. For example, the electric dipole moment p points from the negative charge to the positive charge, and has magnitude p = qd, where q is the charge magnitude and d is the separation distance. An electric dipole is effectively a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance.
Chemistry[edit]
In chemistry, a dipole refers to the separation of charges within a molecule between two covalently bonded atoms. Here, the molecular dipole moment may be defined as a measure of the polarity of the molecule. For example, the water molecule (H2O) has a large dipole moment due to the polar covalent bonds between hydrogen and oxygen.
Dipole Antenna[edit]
A dipole antenna is a radio antenna that can be made of a simple wire, with a center-fed driven element. It consists of two metal conductors of rod or wire, oriented parallel and collinear with each other (in line with each other), with a small space between them.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />