Internal pudendal artery: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Medical terminology]] | [[Category:Medical terminology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Internal_iliac_branches.PNG|Diagram showing branches of the internal iliac artery | |||
File:Gray542.png|The internal pudendal artery and its branches | |||
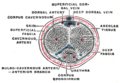
File:Gray236.png|The arteries of the pelvis | |||
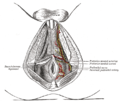
File:Gray829.png|The perineum | |||
File:Gray543.png|The internal pudendal artery | |||
File:Gray1158.png|The arteries of the male pelvis | |||
File:Gray588.png|The arteries of the female pelvis | |||
File:Slide8khi.JPG|Internal pudendal artery | |||
File:Grant_1962_228.png|Internal pudendal artery | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:22, 18 February 2025
Internal Pudendal Artery
The Internal Pudendal Artery is a significant artery in the human body. It is a branch of the internal iliac artery that provides blood supply to the pelvis and perineum.
Anatomy[edit]
The internal pudendal artery originates from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It leaves the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, below the piriformis muscle, and reenters through the lesser sciatic foramen. It then divides into several branches, including the inferior rectal artery, perineal artery, and dorsal artery of the penis or clitoris.
Function[edit]
The internal pudendal artery supplies blood to the external genitalia, the lower part of the rectum, and parts of the perineum. It also plays a crucial role in the erection process in males.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The internal pudendal artery can be involved in various medical conditions. For instance, it can be affected by atherosclerosis, leading to erectile dysfunction in males. It can also be damaged during childbirth or pelvic surgery, leading to hemorrhage or ischemia.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
-
Diagram showing branches of the internal iliac artery
-
The internal pudendal artery and its branches
-
The arteries of the pelvis
-
The perineum
-
The internal pudendal artery
-
The arteries of the male pelvis
-
The arteries of the female pelvis
-
Internal pudendal artery
-
Internal pudendal artery