Tartaric acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Tartaric_acid.svg|Tartaric acid structure | |||
File:TartrateCrystal.svg|Tartrate crystal | |||
File:L-tartaric_acid.png|L-tartaric acid | |||
File:D-tartaric_acid.png|D-tartaric acid | |||
File:Meso-Weinsäure_Spiegel.svg|Meso-tartaric acid | |||
File:Brechweinstein.jpg|Potassium bitartrate (cream of tartar) | |||
File:CommercialTartaric.jpg|Commercial tartaric acid | |||
File:HomemadeTartaric.jpg|Homemade tartaric acid | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:15, 18 February 2025
Tartaric Acid is a white, crystalline organic acid that occurs naturally in many fruits, most notably in grapes, but also in bananas, tamarinds, and citrus. Its salt, potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar, develops naturally in the process of winemaking. It is commonly mixed with sodium bicarbonate and is sold as baking powder used as a leavening agent in food preparation. The acid itself is added to foods as an antioxidant E334 and to impart its distinctive sour taste.
History[edit]
Tartaric acid was first isolated from potassium tartrate, known as tartar, around 800 AD by the Persian alchemist Jabir ibn Hayyan. The modern process was developed in 1769 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The British wine merchant Louis Pasteur was the first to produce tartaric acid using fermentation and aging of wine.
Properties and production[edit]
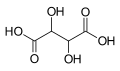
Tartaric acid is a dihydroxy derivative of dicarboxylic acid. It is a useful raw material in organic chemistry for the synthesis of other chiral molecules. The naturally occurring form of the acid is L-(+)-tartaric acid or dextrotartaric acid. The mirror-image form, levotartaric acid or D-(-)-tartaric acid, and the achiral form, mesotartaric acid, do not occur naturally. Tartaric acid is almost always seen as its salt, known as cream of tartar. As a food additive, it is mixed with baking soda to function as a leavening agent.
Uses[edit]
Tartaric acid and its salts have a wide range of uses. In food preparation, they are used as a leavening agent, a flavor enhancer, a preservative, and an emulsifier. In winemaking, they are used to improve the taste of the wine and to stabilize the aging process. In pharmaceuticals, they are used as an excipient and an antioxidant. In cosmetics, they are used as an antioxidant and a pH adjuster.
Safety[edit]
Tartaric acid is generally considered safe for consumption. However, excessive consumption can lead to tartaric acidemia, a rare metabolic disorder.