Corpora quadrigemina: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray709.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
File:Gray707.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
File:Gray678.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
File:Gray710.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
File:Gray713.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
File:Gray716.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
File:Gray720.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
File:Gray792.png|Corpora quadrigemina | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:14, 18 February 2025
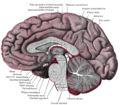
Corpora quadrigemina is a region located in the midbrain, which is part of the brainstem. It is composed of four colliculi, hence the name "quadrigemina". The four colliculi are divided into two superior colliculi and two inferior colliculi. The superior colliculi are involved in visual processing, while the inferior colliculi are involved in auditory processing.
Structure[edit]
The corpora quadrigemina is made up of four rounded eminences, known as colliculi. The two superior colliculi are located on the posterior aspect of the midbrain, while the two inferior colliculi are located just below them. The superior colliculi are part of the visual system and are involved in the reflexive movement of the eyes and head towards a visual stimulus. The inferior colliculi are part of the auditory system and are involved in the reflexive movement of the head and trunk towards an auditory stimulus.
Function[edit]
The superior colliculi are involved in visual processing. They receive input from the retina, the visual cortex, and the spinal cord, and send output to the cranial nerves that control eye movement. The inferior colliculi are involved in auditory processing. They receive input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as input from the auditory cortex, and send output to the thalamus, which then relays auditory information to the auditory cortex.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the corpora quadrigemina can result in a variety of neurological symptoms, depending on the extent and location of the damage. These can include difficulties with eye movement, hearing loss, and problems with coordination and balance.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />