Interstitial lung disease: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Occupational diseases]] | [[Category:Occupational diseases]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:End-stage_interstitial_lung_disease_(honeycomb_lung).jpg|End-stage interstitial lung disease (honeycomb lung) | |||
File:2_SVH_Lung_Health_Interstitial_Lung_Disease_final_1080.jpg|Interstitial lung disease | |||
File:Alveolus_diagram.svg|Alveolus diagram | |||
File:Usual_interstitial_pneumonia_(1).JPG|Usual interstitial pneumonia | |||
File:PCP_CAP_CXR.JPG|Interstitial lung disease | |||
File:IPF_amiodarone.JPG|Interstitial lung disease | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:11, 18 February 2025
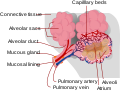
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a group of lung diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the air sacs of the lungs). It concerns over 200 different conditions.
Causes
The exact cause of ILD is often unknown, but they can be categorized into four main areas: exposure to occupational and environmental toxins, autoimmune diseases, medications, and idiopathic (unknown cause).
Occupational and Environmental Toxins
Certain jobs and exposures are linked to ILD, such as mining, farming, and working with asbestos.
Autoimmune Diseases
ILD can be a complication of various autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, and lupus.
Medications
Some drugs can cause ILD, including chemotherapy drugs, heart medications, some antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Idiopathic
In many cases, the cause of ILD is unknown. These are termed idiopathic interstitial pneumonias, the most common of which is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of ILD include shortness of breath, cough, and fatigue. In some cases, clubbing (widening and rounding) of the fingers and toes may occur.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ILD typically involves imaging tests, lung function tests, and sometimes a lung biopsy. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is often used.
Treatment
Treatment for ILD is aimed at preserving lung function and quality of life, and can include medication, pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, and in severe cases, lung transplant.
Prognosis
The prognosis for ILD varies widely depending on the specific type of disease, its cause, and the individual patient's health. Some forms of ILD can lead to respiratory failure and death.
See Also
-
End-stage interstitial lung disease (honeycomb lung)
-
Interstitial lung disease
-
Alveolus diagram
-
Usual interstitial pneumonia
-
Interstitial lung disease
-
Interstitial lung disease