Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
* [[Dysphagia]] | * [[Dysphagia]] | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray186.png|Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |||
File:Gray385.png|Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |||
File:Slide12mmm.JPG|Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |||
File:Slide4iiii.JPG|Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |||
File:Slide1kuku.JPG|Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |||
File:Slide2kuku.JPG|Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |||
File:Slide3kuku.JPG|Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:11, 18 February 2025
Middle Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle[edit]
The middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle is one of the three pharyngeal constrictor muscles located in the throat. It plays a crucial role in the process of swallowing and helps in the movement of food and liquids from the mouth to the esophagus. In this article, we will explore the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle.
Anatomy[edit]
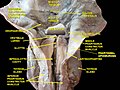
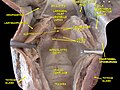
The middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a thin, fan-shaped muscle that forms a part of the pharyngeal wall. It is situated between the superior and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles. The muscle fibers originate from the hyoid bone and extend posteriorly to attach to the pharyngeal raphe, a fibrous midline structure in the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle is to aid in the process of swallowing. During swallowing, the muscle contracts, narrowing the diameter of the pharynx and exerting pressure on the bolus of food or liquid. This action helps propel the bolus towards the esophagus, facilitating its passage through the digestive system.
Additionally, the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle also assists in the closure of the nasopharynx during swallowing. It contracts to prevent the entry of food or liquid into the nasal cavity, ensuring that the bolus is directed towards the esophagus and not the respiratory system.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle can be affected by various medical conditions, leading to functional impairments. Some common clinical conditions associated with this muscle include:
- Pharyngeal dysphagia: Dysfunction of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle can result in difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia. This condition can cause discomfort, choking, and aspiration of food or liquid into the airway.
- Pharyngeal diverticulum: Weakness or structural abnormalities of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle can lead to the formation of a pharyngeal diverticulum. This is a pouch-like protrusion that develops in the pharyngeal wall, causing swallowing difficulties and regurgitation of food.
- Pharyngoesophageal stricture: Inflammation or scarring of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle can result in the narrowing of the pharynx, leading to a condition called pharyngoesophageal stricture. This condition can cause difficulty swallowing and may require medical intervention.
References[edit]
1. Standring, S. (Ed.). (2016). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (41st ed.). Elsevier.
2. Drake, R. L., Vogl, W., & Mitchell, A. W. M. (2014). Gray's Anatomy for Students (3rd ed.). Elsevier.
See Also[edit]
- Pharyngeal constrictor muscles
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Swallowing
- Dysphagia
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle