Copper monosulfide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Sulfid_měďnatý.PNG|Copper monosulfide | |||
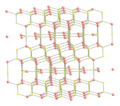
File:Covellite-xtal-CM-3D-balls.png|Covellite crystal structure | |||
File:Covellite-Cu1-coordination-3D-balls.png|Covellite Cu1 coordination | |||
File:Covellite-Cu2-coordination-3D-balls.png|Covellite Cu2 coordination | |||
File:Covellite-S1-coordination-3D-balls.png|Covellite S1 coordination | |||
File:Covellite-S2-coordination-3D-balls.png|Covellite S2 coordination | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:09, 18 February 2025
Copper monosulfide (CuS) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuS. It is known as a mineral under the name covellite and has a distinctive deep indigo blue color. Copper monosulfide is found in nature as a minor ore of copper and is also produced synthetically for various applications. This compound is of interest not only for its industrial applications but also for its occurrence in natural processes, including those within biological systems.
Properties[edit]
Copper monosulfide is a semiconductor and exhibits a range of electrical properties that can be manipulated by doping with other elements. It has a hexagonal crystal structure and is relatively stable under normal conditions. However, it can react with strong acids to produce hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S), a toxic and flammable substance.
Synthesis[edit]
Copper monosulfide can be synthesized through several methods. One common approach involves the direct combination of copper and sulfur at high temperatures. Another method is the precipitation of copper(II) ions with sulfide ions in aqueous solution, which results in the formation of CuS along with copper(II) sulfide (CuS2).
Applications[edit]
- Industrial Uses
Copper monosulfide is used in the manufacture of solar cells, where it serves as a p-type semiconductor material. It is also utilized in the production of superconductors and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
- Biological Significance
In biology, copper monosulfide has been studied for its role in copper homeostasis and metabolism in organisms. It is involved in the formation of copper proteins that are essential for biological functions, including respiration and antioxidant defense.
Health and Safety[edit]
Exposure to copper monosulfide should be managed with care, as it can be toxic if ingested or inhaled. The compound can release hydrogen sulfide gas when reacting with acids, posing risks of inhalation hazards. Appropriate safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), are recommended when handling CuS.
Environmental Impact[edit]
The mining and processing of copper monosulfide can have environmental impacts, including the release of sulfur compounds into the atmosphere. Proper waste management and pollution control measures are essential to minimize its environmental footprint.
-
Copper monosulfide
-
Covellite crystal structure
-
Covellite Cu1 coordination
-
Covellite Cu2 coordination
-
Covellite S1 coordination
-
Covellite S2 coordination