Supraclavicular nerves: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray805.png|Supraclavicular nerves | |||
File:Gray804.png|Supraclavicular nerves | |||
File:Gray784.png|Supraclavicular nerves | |||
File:Gray811and813.PNG|Supraclavicular nerves | |||
File:Gray812and814.svg|Supraclavicular nerves | |||
File:Gray1210.png|Supraclavicular nerves | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:04, 18 February 2025
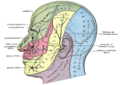
Supraclavicular nerves are a group of nerves that originate from the cervical plexus, specifically from the third and fourth cervical nerves. They are responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin over the upper chest and shoulder.
Etymology[edit]
The term "supraclavicular" is derived from the Latin words "supra" meaning above and "clavicula" meaning little key, referring to the location of these nerves above the clavicle.
Anatomy[edit]
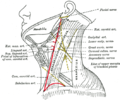
The supraclavicular nerves emerge from the lateral border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, cross over the sternoclavicular joint, and divide into medial, intermediate, and lateral branches. These branches provide sensory innervation to the skin over the upper chest and shoulder.
Medial Branch[edit]
The medial branch of the supraclavicular nerves, also known as the anterior supraclavicular nerves, innervates the skin over the anterior and middle parts of the deltoid muscle.
Intermediate Branch[edit]
The intermediate branch, also known as the middle supraclavicular nerves, innervates the skin over the lateral part of the pectoralis major muscle and the upper part of the deltoid.
Lateral Branch[edit]
The lateral branch, also known as the posterior supraclavicular nerves, innervates the skin over the lower part of the deltoid and the upper part of the latissimus dorsi muscle.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Damage to the supraclavicular nerves can result in sensory loss or paresthesia in the areas of the skin they innervate. This can occur due to trauma, surgery, or conditions such as brachial plexus injury.