Mosquito-borne disease: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[Category:Tropical medicine]] | [[Category:Tropical medicine]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
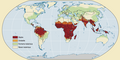
File:World-map-of-past-and-current-malaria-prevalence-world-development-report-2009.png|World map of past and current malaria prevalence | |||
File:Dengue06.png|Dengue fever distribution map | |||
File:Yellow_fever_Africa_2005.png|Yellow fever distribution in Africa, 2005 | |||
File:Yellow_fever_South_America_2005.png|Yellow fever distribution in South America, 2005 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:01, 18 February 2025
Mosquito-borne diseases are illnesses caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites transmitted by mosquitoes. Nearly 700 million people get a mosquito-borne illness each year resulting in over one million deaths. Diseases transmitted by mosquitoes include malaria, dengue fever, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, filariasis, Zika virus, and others.
Transmission[edit]
Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on a person or animal already infected with the disease. After the virus or parasite matures inside the mosquito, it can be transmitted to other people or animals through the mosquito's bites. Different species of mosquitoes are vectors for different diseases. For example, Aedes mosquitoes are responsible for the transmission of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses, while Anopheles mosquitoes are vectors for malaria.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of mosquito-borne diseases primarily involves controlling mosquito populations and limiting exposure to bites. Strategies include the use of insect repellent, wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, using mosquito nets, and eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed. Community-wide efforts may include spraying insecticides and introducing natural predators of mosquitoes.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment varies depending on the specific disease. For many mosquito-borne diseases, treatment is primarily supportive and can include rest, fluids, and use of pain relievers and fever reducers. In the case of more severe diseases like malaria, specific antimalarial medications are required. There is no specific treatment for some viral diseases such as dengue fever, and care is focused on relieving symptoms.
Impact[edit]
Mosquito-borne diseases have a significant impact on public health globally, especially in tropical and subtropical regions where mosquito populations are high year-round. These diseases can cause widespread outbreaks that strain healthcare systems, lead to economic losses, and result in significant morbidity and mortality.
Research[edit]
Ongoing research aims to develop more effective ways to control mosquitoes and prevent diseases they transmit. This includes the development of vaccines, such as the RTS,S vaccine for malaria, and innovative control strategies like genetically modified mosquitoes or the use of Wolbachia bacteria to inhibit disease transmission.
See also[edit]
-
World map of past and current malaria prevalence
-
Dengue fever distribution map
-
Yellow fever distribution in Africa, 2005
-
Yellow fever distribution in South America, 2005