Ceric ammonium nitrate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ceric_ammonium_nitrate.jpg|Ceric ammonium nitrate | |||
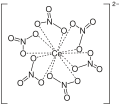
File:Hexanitratocerat.svg|Hexanitratocerat structure | |||
File:Hexanitratocerate(IV)-ion-from-CAN-xtal-3D-bs-17.png|Hexanitratocerate(IV) ion 3D structure | |||
File:Wulff–Dötz_reaction_to_a_chromium_half-sandwich_complex.png|Wulff–Dötz reaction to a chromium half-sandwich complex | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:59, 18 February 2025
Ceric Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6. It is a powerful oxidizing agent used in a variety of chemical reactions. CAN appears as a red-orange crystalline solid at room temperature. Due to its strong oxidizing properties, it is commonly employed in organic chemistry for the oxidation of alcohols, phenols, and other functional groups. Additionally, it finds applications in analytical chemistry, materials science, and as a reagent in the synthesis of complex organic compounds.
Properties[edit]
Ceric ammonium nitrate is highly soluble in water and organic solvents, which makes it a versatile reagent in both aqueous and non-aqueous chemistry. Its oxidizing strength is attributed to the cerium ion (Ce^4+), which can undergo reduction to Ce^3+ while oxidizing other species. This redox versatility is key to its widespread use in chemical transformations.
Applications[edit]
Organic Synthesis[edit]
In organic chemistry, CAN is utilized for the oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes, secondary alcohols to ketones, and the transformation of certain sulfur and nitrogen compounds. Its selectivity and mild reaction conditions make it a preferred oxidant for sensitive substrates.
Analytical Chemistry[edit]
CAN serves as a standard oxidizing agent in analytical chemistry for the determination of certain compounds through redox titrations. It is also used in the quantitative analysis of pharmaceuticals and other complex mixtures.
Materials Science[edit]
In materials science, ceric ammonium nitrate has been explored for the synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles and the modification of polymer surfaces. Its ability to initiate polymerization reactions is particularly valuable for creating novel polymeric materials.
Safety and Handling[edit]
Ceric ammonium nitrate is a strong oxidizer and should be handled with care. It can cause fire or explosion when in contact with combustible materials. Appropriate safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and storage in a cool, dry place, are essential when working with this compound.
Environmental Impact[edit]
The environmental impact of ceric ammonium nitrate is primarily associated with its disposal. As an oxidizing agent, it can pose risks to aquatic life and should not be discharged into the environment without proper treatment. Waste management practices should follow local regulations and guidelines to minimize its environmental footprint.
-
Ceric ammonium nitrate
-
Hexanitratocerat structure
-
Hexanitratocerate(IV) ion 3D structure
-
Wulff–Dötz reaction to a chromium half-sandwich complex