2-Iodoxybenzoic acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[Category:Organoiodine compounds]] | [[Category:Organoiodine compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Oxidizing agents]] | [[Category:Oxidizing agents]] | ||
== 2-Iodoxybenzoic_acid == | |||
<gallery> | |||
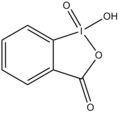
File:IBXAcid.png|2-Iodoxybenzoic acid structure | |||
File:IBX_Preparation.png|Preparation of 2-Iodoxybenzoic acid | |||
File:IBX-Oxidation_2a.svg|IBX oxidation mechanism | |||
File:IBXacid_example.svg|Example of IBX acid reaction | |||
File:IBX_oxidative_cleavage.png|IBX oxidative cleavage | |||
File:IBX_DMSO_oxidative_cleavage.png|IBX DMSO oxidative cleavage | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:59, 18 February 2025
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid[edit]

2-Iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) is an organoiodine compound that is widely used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry. It is a hypervalent iodine compound, specifically a _5-iodane, and is known for its ability to selectively oxidize alcohols to aldehydes or ketones.
Structure and Properties[edit]
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid is characterized by the presence of an iodine atom in a +5 oxidation state, bonded to an aromatic ring. The iodine atom is also bonded to two oxygen atoms, forming an iodine-oxygen double bond and an iodine-oxygen single bond, which gives the compound its oxidizing properties.
Synthesis[edit]

2-Iodoxybenzoic acid is typically synthesized from 2-iodobenzoic acid through oxidation. The oxidation is often carried out using strong oxidizing agents such as sodium periodate or potassium bromate in an acidic medium.
Applications in Organic Synthesis[edit]
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid is primarily used as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis. It is particularly effective in the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones, respectively.
Oxidation of Alcohols[edit]

IBX is known for its mild and selective oxidation of alcohols. It can oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes without over-oxidizing them to carboxylic acids. Secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones.
Oxidative Cleavage[edit]

IBX can also be used for the oxidative cleavage of vicinal diols, leading to the formation of two carbonyl compounds. This reaction is useful in the degradation of complex molecules into simpler fragments.
Use in Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)[edit]

In the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), IBX can facilitate the oxidative cleavage of certain substrates, providing a versatile method for the transformation of organic compounds.
Safety and Handling[edit]
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid is a powerful oxidizing agent and should be handled with care. It is important to use appropriate personal protective equipment and to work in a well-ventilated area to avoid exposure to its potentially harmful effects.
Related pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Example of IBX oxidation
2-Iodoxybenzoic_acid[edit]
-
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid structure
-
Preparation of 2-Iodoxybenzoic acid
-
IBX oxidation mechanism
-
Example of IBX acid reaction
-
IBX oxidative cleavage
-
IBX DMSO oxidative cleavage