Anterior cruciate ligament injury: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
== Anterior_cruciate_ligament_injury == | |||
<gallery> | |||
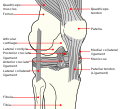
File:Knee_diagram.svg|Diagram of the knee showing ligaments | |||
File:ACL_Tear.png|Image of an ACL tear | |||
File:Labelled_Femur_Q_Angle.jpg|Labelled diagram showing the Q angle of the femur | |||
File:Gray347.png|Anatomical illustration of the knee joint | |||
File:Gray348.png|Detailed anatomy of the knee joint | |||
File:VKB-Riss_MRT_T1_PDW_sag.jpg|MRI image showing ACL injury | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 04:58, 18 February 2025
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the key ligaments that help stabilize the knee joint. ACL injuries are among the most common knee injuries, especially in athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball. ACL injuries can range from mild (such as small tears/sprains) to severe (complete tears). The severity of the injury dictates the treatment and recovery process.
Causes
ACL injuries are most commonly caused by:
- Sudden stops or changes in direction
- Jumping and landing incorrectly
- Direct collision, such as during a football tackle
Symptoms
Symptoms of an ACL injury include:
- A loud "pop" or a "popping" sensation in the knee
- Severe pain and inability to continue activity
- Rapid swelling
- Loss of range of motion
- A feeling of instability or "giving way" with weight bearing
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of an ACL injury involves a physical examination and often imaging tests such as:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): To visualize the extent of the injury.
- X-ray: To rule out any bone fractures.
Treatment
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's needs. They include:
- Non-surgical treatment: Rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee.
- Surgical treatment: ACL reconstruction surgery to replace the torn ligament with a piece of tendon from another part of the body or a donor.
Recovery
Recovery from an ACL injury can take several months. A combination of physical therapy, rehabilitation exercises, and, if necessary, surgery, can help an individual return to normal activities.
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- Strengthening leg muscles
- Proper training and exercise techniques
- Using proper sports equipment
See Also
Anterior_cruciate_ligament_injury
-
Diagram of the knee showing ligaments
-
Image of an ACL tear
-
Labelled diagram showing the Q angle of the femur
-
Anatomical illustration of the knee joint
-
Detailed anatomy of the knee joint
-
MRI image showing ACL injury