GTPase-activating protein: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{enzyme-stub}} | {{enzyme-stub}} | ||
{{cellbio-stub}} | {{cellbio-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:G_proteins_and_GAP_hydrolytic_activity.png|GTPase-activating protein | |||
File:GAP_mechanism_of_activity.png|GTPase-activating protein | |||
File:Normal_G_protein_activity.png|GTPase-activating protein | |||
File:G_proteins_without_GAP.png|GTPase-activating protein | |||
File:Non-hydrolytic_G_proteins.png|GTPase-activating protein | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:57, 18 February 2025
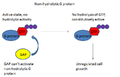
GTPase-activating protein (GAP) is a type of enzyme that regulates the activity of G proteins by increasing their rate of GTP hydrolysis. This process is crucial for the regulation of fundamental cellular processes such as signal transduction, cell division, and protein synthesis.
Function[edit]
GAPs function by binding to activated G proteins and stimulating their intrinsic GTPase activity, thereby accelerating the conversion of bound GTP to GDP. This results in the inactivation of the G protein and termination of the signaling event.
Types of GTPase-activating proteins[edit]
There are several types of GTPase-activating proteins, each with a specific set of target G proteins. These include:
- RhoGAP: These GAPs specifically target Rho family of G proteins, which are involved in regulating the cytoskeleton and cell migration.
- RasGAP: These GAPs target Ras subfamily of G proteins, which are involved in cell growth, differentiation, and survival.
- RabGAP: These GAPs target Rab family of G proteins, which are involved in vesicle trafficking.
Clinical significance[edit]
Mutations in GTPase-activating proteins have been implicated in several diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. For example, mutations in the NF1 gene, which encodes a RasGAP, are associated with Neurofibromatosis type I, a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of tumors along nerves in the skin, brain, and other parts of the body.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
This article is a Cell biology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
```
-
GTPase-activating protein
-
GTPase-activating protein
-
GTPase-activating protein
-
GTPase-activating protein
-
GTPase-activating protein