GABA: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gamma-Aminobuttersäure_-_gamma-aminobutyric_acid.svg|Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Structure | |||
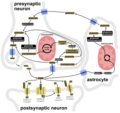
File:Release,_Reuptake,_and_Metabolism_Cycle_of_GABA.png|Release, Reuptake, and Metabolism Cycle of GABA | |||
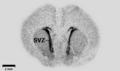
File:Autoradiography_of_a_brain_slice_from_an_embryonal_rat_-_PMID19190758_PLoS_0004371.png|Autoradiography of a Brain Slice from an Embryonal Rat | |||
File:Gabaergic_Neurons.png|Gabaergic Neurons | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:56, 18 February 2025
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric acid) is a naturally occurring amino acid that works as a neurotransmitter in your brain. Neurotransmitters function as chemical messengers. GABA is considered an inhibitory neurotransmitter because it blocks, or inhibits, certain brain signals and decreases activity in your nervous system.
Function[edit]
When GABA attaches to a protein in your brain known as a GABA receptor, it produces a calming effect. This can help with feelings of anxiety, stress, and fear. It may also help to prevent seizures.
GABA and Health[edit]
Certain medications used to treat conditions like epilepsy, anxiety, and mood disorders work by increasing the action of GABA in the brain. These include drugs like benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and certain antidepressants.
GABA Supplements[edit]
GABA supplements are often used to help reduce stress and anxiety. However, there is limited scientific research to support these uses. Some research suggests that GABA produced in fermented foods may increase sleep time and decrease the time it takes to fall asleep. More research is needed to fully understand these effects.