Ilioinguinal nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Medical terminology]] | [[Category:Medical terminology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Lumbar_plexus.svg|Diagram of the lumbar plexus | |||
File:Gray823.png|Ilioinguinal nerve and its branches | |||
File:Gray824.png|Course of the ilioinguinal nerve | |||
File:Gray825and830.PNG|Anatomy of the ilioinguinal nerve | |||
File:Gray826and831.svg|Ilioinguinal nerve in relation to other structures | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:38, 18 February 2025
Ilioinguinal nerve
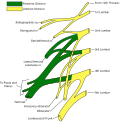
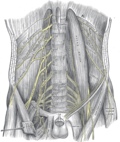
The Ilioinguinal nerve is a branch of the first lumbar nerve (L1). It separates from the lumbar plexus along with the iliohypogastric nerve and descends obliquely across the quadratus lumborum and iliacus muscles.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Ilioinguinal" is derived from the Latin words "ilium", meaning flank, and "inguinal", meaning groin. Thus, the term refers to a nerve that runs from the flank to the groin.
Anatomy[edit]
The Ilioinguinal nerve passes obliquely across the quadratus lumborum and iliacus muscles. It then pierces the transversus abdominis to run above the inguinal ligament and ends in the skin of the upper medial thigh, the root of the penis and anterior scrotum in males, and the mons pubis and labia majora in females.
Function[edit]
The Ilioinguinal nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the upper medial part of the thigh and the root of the penis and anterior scrotum in males or the mons pubis and labia majora in females. It also supplies the skin over the symphysis pubis.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the Ilioinguinal nerve can result in ilioinguinal nerve entrapment, which can cause pain in the groin area. This condition is often caused by local trauma or surgery, such as hernia repair. Treatment options include nerve block, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical neurectomy.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />