Exponential growth: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[Category:Physics]] | [[Category:Physics]] | ||
[[Category:Economics]] | [[Category:Economics]] | ||
== Exponential_growth == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Exponential.svg|Exponential growth curve | |||
File:e.coli-colony-growth.gif|E. coli colony growth | |||
File:Exponentielles_wachstum2.svg|Exponential growth illustration | |||
File:Exponentieller_zerfall2.svg|Exponential decay illustration | |||
File:Verhulst-Malthus.svg|Verhulst-Malthus logistic growth model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:35, 18 February 2025
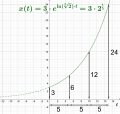
Exponential growth is a specific way that a quantity may increase over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (as in f(t) = aekt).
Mathematical Description[edit]
In an exponential growth process, the growth rate of the value is proportional to the current value resulting in the value at any time being an exponential function of time, i.e., f(t) = aekt, where a is the value at the start, k is the rate of growth (the constant of proportionality), and t is time.
In Biology[edit]
Biological populations, including that of humans, are subject to exponential growth until resources become scarce. From the 17th century to the 19th century, human population began to grow rapidly due to improvements in sanitation and healthcare - the global population doubling in size during the 20th century.
In Medicine[edit]
In medicine, understanding exponential growth is important for understanding certain biological processes, including the spread of diseases. For example, the number of cases of a disease can grow exponentially in the early stages of an epidemic, before the disease becomes widespread and the growth slows down.
In Physics[edit]
In physics, exponential growth is seen in any quantity that grows at a rate proportional to its current value. One example of this is the concept of compound interest.
In Economics[edit]
In economics, "exponential growth" is used metaphorically to describe economic growth. In the world of finance and investment, exponential growth is often associated with things like compound interest or the growth of investments.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />