European Health Insurance Card: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category:European Union law]] | [[Category:European Union law]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:EHIC_Slovenia.jpg|European Health Insurance Card - Slovenia | |||
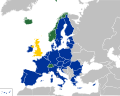
File:EHIC_participants.svg|Map of European Health Insurance Card participants | |||
File:Elektronische_Gesundheitskarte_Mustermann_RS.svg|Sample Electronic Health Card - Germany | |||
File:Carte_Européenne_d'Assurance_Maladie_France.svg|European Health Insurance Card - France | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:34, 18 February 2025
European Health Insurance Card
The European Health Insurance Card (EHIC) is a free card that gives insurance holders the right to access state-provided healthcare during a temporary stay in any of the European Union (EU) countries, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland, under the same conditions and at the same cost (free in some countries) as people insured in that country. Cards are issued by the national health insurance providers. The EHIC covers treatment that is medically necessary until the cardholder's planned return home. This includes treatment for pre-existing medical conditions and for routine maternity care, as long as the reason for the visit is not specifically to give birth or seek treatment.
Background[edit]
The EHIC was introduced on 1 June 2004, replacing the old E111 forms and several other pre-existing forms, simplifying the process of obtaining medical care while abroad within the scheme's participating countries. The initiative aims to facilitate access to medical services for travelers within the EU and associated countries, ensuring that individuals do not face large medical bills due to illness or injury while abroad.
Eligibility[edit]
To be eligible for an EHIC, an individual must be insured by or covered by a state social security system in any member state of the EU, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, or Switzerland. The card is not issued to non-EU nationals who reside outside the EU unless they are covered by a state social security system in an EU member state.
Usage[edit]
The EHIC must be presented at the time of treatment, along with any other identification required by the healthcare provider. It is important to note that the EHIC is not an alternative to travel insurance. It does not cover any private healthcare or costs such as a return flight to your home country or lost/stolen property. It also does not cover your costs if you are traveling for the express purpose of obtaining medical treatment.
Application[edit]
The application process for an EHIC varies from country to country. In most cases, the card can be applied for through the national health insurance provider's website. The card is usually valid for up to 5 years and can be renewed.
Limitations[edit]
While the EHIC provides a valuable service for travelers, it has its limitations. It should be seen as a complement to, rather than a replacement for, comprehensive travel insurance. For example, it will not cover the costs of repatriation or specific medical procedures that are not covered under the state healthcare system of the visited country.
Brexit[edit]
Following the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the European Union (Brexit), the validity of the EHIC for UK citizens has changed. UK citizens can no longer apply for a new EHIC, but those issued before the end of 2020 remain valid until their expiry date. A new scheme, the Global Health Insurance Card (GHIC), has been introduced for UK residents.
See Also[edit]
-
European Health Insurance Card - Slovenia
-
Map of European Health Insurance Card participants
-
Sample Electronic Health Card - Germany
-
European Health Insurance Card - France