Nuclear-weapon-free zone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:International security]] | [[Category:International security]] | ||
{{nuclear-stub}} | {{nuclear-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:nwfz.svg|Nuclear-weapon-free zone map | |||
File:Exclusive_Economic_Zones.svg|Exclusive Economic Zones | |||
File:Equator-60S-20W-115E-48.png|Equator and surrounding coordinates | |||
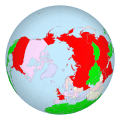
File:Nws_polar.svg|Nuclear-weapon states polar projection | |||
File:North_Atlantic_Treaty_Organization_(orthographic_projection).svg|North Atlantic Treaty Organization map | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:34, 18 February 2025
Nuclear-weapon-free zone (NWFZ) is a designated region in which the production, acquisition, and deployment of nuclear weapons are prohibited. The concept of NWFZs was first proposed in the United Nations in the context of Cold War tensions, as a means to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promote nuclear disarmament.
History[edit]
The first NWFZ was established in Antarctica by the Antarctic Treaty of 1959. This was followed by the Treaty of Tlatelolco in 1967, which established a NWFZ in Latin America and the Caribbean. Since then, several other regions have been declared NWFZs, including the South Pacific (Treaty of Rarotonga, 1985), Southeast Asia (Treaty of Bangkok, 1995), and Africa (Treaty of Pelindaba, 1996).
Characteristics[edit]
NWFZs are governed by international treaties, which typically include provisions for verification and enforcement. The treaties also often include positive security assurances from nuclear-weapon states, pledging not to use or threaten to use nuclear weapons against the parties to the treaty.
Criticisms and Controversies[edit]
While NWFZs have been praised for their role in preventing nuclear proliferation, they have also been criticized on several grounds. Some critics argue that they are ineffective in the absence of global disarmament, while others contend that they may actually encourage proliferation by creating a sense of complacency.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
This article is a nuclear physics or atomic physics–related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Nuclear-weapon-free zone map
-
Exclusive Economic Zones
-
Equator and surrounding coordinates
-
Nuclear-weapon states polar projection
-
North Atlantic Treaty Organization map