Osteoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ostéome.jpg|Osteoma | |||
File:Osteom_der_Stirnhoehle_Roentgen.jpg|Osteoma of the frontal sinus X-ray | |||
File:Osteom_der_Stirnhoehle_CT.jpg|Osteoma of the frontal sinus CT | |||
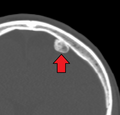
File:OsteomaMark.png|Osteoma | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 04:32, 18 February 2025
Osteoma is a new piece of bone usually growing on another piece of bone, typically the skull. It is a benign tumor.
Causes
While the exact cause of osteoma is not known, it is believed to be a result of previous trauma or infection. Some researchers also suggest a genetic link, as osteomas are more common in certain families.
Symptoms
Osteomas may cause pain and deformity, depending on their size and location. They may also cause problems with hearing, vision, or other functions if they grow near nerves or other sensitive structures.
Diagnosis
Osteomas are usually discovered during routine medical examinations, as they often do not cause any symptoms. They can be seen on X-rays, CT scans, and other imaging studies. A biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for osteoma depends on the size and location of the tumor. Small osteomas that do not cause symptoms may not require treatment. Larger osteomas or those that cause symptoms may need to be removed surgically.
See also
References
<references />