Hydrogen atom: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery caption="Hydrogen_atom"> | |||
File:Hydrogen_eigenstate_n4_l3_m1.png|Hydrogen eigenstate n=4, l=3, m=1 | |||
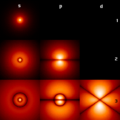
File:HAtomOrbitals.png|Hydrogen atom orbitals | |||
File:Azsxdcv.gif|Hydrogen_atom | |||
File:Spherical_harmonics_animation1.gif|Spherical harmonics animation | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:30, 18 February 2025
Hydrogen Atom
The Hydrogen atom is the simplest and most fundamental atom in the universe. It is composed of a single proton and a single electron, making it the lightest and most abundant element in the universe.
Structure[edit]
The hydrogen atom consists of a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron. These two particles are held together by the electromagnetic force, which causes the electron to orbit the proton in a manner similar to how the Earth orbits the Sun.
Energy Levels[edit]
The energy levels of a hydrogen atom are quantized, meaning they can only take on certain discrete values. This is a result of the quantum mechanical nature of electrons. The energy levels are often represented by the principal quantum number n, which can take on any positive integer value. The energy of the electron in the nth energy level is given by the formula:
- E = -13.6 eV / n²
where E is the energy, eV is electron volts, and n is the principal quantum number.
Spectral Lines[edit]
When a hydrogen atom transitions from a higher energy level to a lower one, it emits a photon with a specific wavelength. These wavelengths correspond to the spectral lines of hydrogen, which are observed in the hydrogen spectrum. The wavelengths of these spectral lines can be calculated using the Rydberg formula.
Isotopes[edit]
There are three isotopes of hydrogen: protium, deuterium, and tritium. Protium is the most common isotope and consists of one proton and one electron. Deuterium has one proton, one neutron, and one electron, while tritium has one proton, two neutrons, and one electron.
Applications[edit]
Hydrogen atoms are crucial in many areas of science and technology. They are used in nuclear fusion reactions, which power the Sun and other stars. They are also used in spectroscopy to study the properties of other atoms and molecules.