Demerara rebellion of 1823: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{Guyana-hist-stub}} | {{Guyana-hist-stub}} | ||
{{food-stub}} | {{food-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Plate_2_Retreat_of_Lt_Brady.jpg|Retreat of Lt. Brady | |||
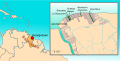
File:Demerara_rebellion_of_1823_map.svg|Map of the Demerara Rebellion of 1823 | |||
File:Plate_6_Provisional_Battalion.jpg|Provisional Battalion | |||
File:Plate_4_Bachelor's_Adventure_zoom.png|Bachelor's Adventure | |||
File:Demerara_1823.jpg|Demerara Rebellion of 1823 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:29, 18 February 2025
Demerara rebellion of 1823
The Demerara rebellion of 1823 was a significant uprising involving more than 10,000 enslaved people that took place in the Crown colony of Demerara-Essequibo (now part of Guyana) in August 1823. This event is considered one of the largest slave rebellions in the history of the British Empire.
Background[edit]
The rebellion took place in a period of growing tension between the enslaved population and the plantation owners. The enslaved people were largely of African descent, brought to the colony to work on the sugar plantations. The plantation owners, mostly British, were known for their harsh treatment of the enslaved people.
The Rebellion[edit]
The rebellion began on August 18, 1823, led by a man named Jack Gladstone, an enslaved man on the plantation of Success. The rebellion spread quickly across the colony, with the enslaved people demanding their freedom and an end to their harsh treatment.
Despite the large number of participants, the rebellion was quickly suppressed by the British forces. The aftermath of the rebellion saw a significant number of enslaved people killed or punished, and the leaders, including Gladstone, were executed.
Impact[edit]
The Demerara rebellion had a significant impact on the British public and led to a change in public opinion towards slavery. The rebellion, and its brutal suppression, was widely reported in the British press, leading to increased calls for the abolition of slavery. This eventually led to the Slavery Abolition Act 1833, which abolished slavery throughout the British Empire.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
This Guyana history-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Retreat of Lt. Brady
-
Map of the Demerara Rebellion of 1823
-
Provisional Battalion
-
Bachelor's Adventure
-
Demerara Rebellion of 1823