Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[Category:Medical procedures]] | [[Category:Medical procedures]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
==Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling== | |||
<gallery> | |||
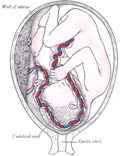
File:Gray38.png|Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling | |||
File:Anterior_Sampling.svg|Anterior sampling technique | |||
File:Posterior_Sampling.svg|Posterior sampling technique | |||
File:Human_male_karyotpe_high_resolution.jpg|Human male karyotype high resolution | |||
File:Single_umbilical_artery,_HE..jpg|Single umbilical artery, HE stain | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:22, 18 February 2025
Percutaneous Umbilical Cord Blood Sampling (PUBS), also known as Cordocentesis, is a diagnostic medical procedure that involves the extraction of fetal blood directly from the umbilical cord. This procedure is typically performed under ultrasound guidance to ensure accuracy and safety. PUBS is utilized in prenatal diagnosis and therapy, offering a method to assess and treat fetal conditions before birth. It is considered when information cannot be obtained through less invasive methods such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Indications[edit]
Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling is indicated in various scenarios, including but not limited to:
- Fetal blood typing in cases of Rh incompatibility
- Detection of fetal infections
- Assessment of anemia in the fetus, particularly due to Rh disease or parvovirus B19 infection
- Diagnosis of genetic or chromosomal abnormalities
- Evaluation of fetal blood gases in cases of suspected fetal distress
- Management and diagnosis of fetal thrombocytopenia
Procedure[edit]
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia in a hospital setting. Using ultrasound imaging for guidance, a thin needle is carefully inserted through the mother's abdomen and uterus, into the umbilical cord to draw a small sample of fetal blood. The entire process is closely monitored to minimize risks to both the fetus and the mother.
Risks and Complications[edit]
While PUBS is a valuable diagnostic tool, it carries risks and potential complications, including:
- Fetal bleeding
- Fetal bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Infection
- Premature rupture of membranes
- Potential for miscarriage or preterm labor
Due to these risks, the decision to proceed with PUBS is made with careful consideration of the benefits and potential harms.
Alternatives[edit]
Alternatives to PUBS include:
- Amniocentesis: Sampling of the amniotic fluid for fetal cells and substances
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): Sampling of placental tissue for genetic and chromosomal information
- Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT): Blood test to screen for certain genetic conditions
Conclusion[edit]
Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling is a specialized procedure used in the diagnosis and treatment of fetal conditions. Despite its risks, PUBS remains an important tool in prenatal care, particularly when other diagnostic methods are insufficient. As with any medical procedure, the decision to undergo PUBS should be made after thorough discussion with a healthcare provider, considering all available options.
Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling[edit]
-
Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling
-
Anterior sampling technique
-
Posterior sampling technique
-
Human male karyotype high resolution
-
Single umbilical artery, HE stain