Nuclear weapon yield: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{military-stub}} | {{military-stub}} | ||
{{physics-stub}} | {{physics-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:US_nuclear_weapons_yield-to-weight_comparison.svg|Comparison of US nuclear weapons yield to weight | |||
File:Comparative_nuclear_fireball_sizes.svg|Comparative nuclear fireball sizes | |||
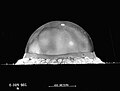
File:Trinity_Test_Fireball_25ms.jpg|Trinity Test Fireball at 25 milliseconds | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:08, 18 February 2025
Nuclear weapon yield refers to the amount of energy released when a nuclear weapon is detonated. This energy is usually expressed in terms of "tons of TNT", where one ton of TNT is equivalent to the energy released in the detonation of 1,000 kilograms of TNT.
Measurement of Nuclear Weapon Yield[edit]
The yield of a nuclear weapon is measured in kilotons (kt) or megatons (Mt), where one kiloton is equivalent to the energy released by 1,000 tons of TNT, and one megaton is equivalent to the energy released by 1,000,000 tons of TNT. The yield can also be measured in joules, with one kiloton of TNT equivalent to approximately 4.18 x 10^12 joules.
Factors Influencing Nuclear Weapon Yield[edit]
The yield of a nuclear weapon is determined by several factors, including the design of the weapon, the materials used in its construction, and the efficiency of the nuclear reactions that occur during detonation. The two primary types of nuclear reactions are fission and fusion, each of which releases a different amount of energy.
Fission[edit]
In a fission reaction, the nucleus of a heavy atom, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, is split into two or more smaller nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. The yield of a fission weapon is primarily determined by the mass and purity of the fissile material used.
Fusion[edit]
In a fusion reaction, two light nuclei, such as deuterium and tritium, combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process. The yield of a fusion weapon, also known as a hydrogen bomb or thermonuclear weapon, is much greater than that of a fission weapon.
Effects of Nuclear Weapon Yield[edit]
The yield of a nuclear weapon determines the extent of the blast wave, thermal radiation, and nuclear radiation produced by the detonation. The larger the yield, the greater the area of destruction and the higher the levels of radiation.
See Also[edit]
-
Comparison of US nuclear weapons yield to weight
-
Comparative nuclear fireball sizes
-
Trinity Test Fireball at 25 milliseconds